Adolescence

Key Points
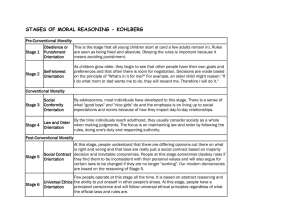
Pre-conventional Moral Reasoning
Conventional moral reasoning
Post-Conventional Morality
Stage 1
Obedience or Punishment Orientation
This is the stage that all young children start at and a few adults remain in.
Rules are seen as being fixed and absolute. Obeying the rules is important because it means avoiding punishment.
"The last time I did that I got spanked so I will not do it again."
Stage 2
Self-Interest Orientation
As children grow older, they begin to see that other people have their own goals and preferences and that often there is room for negotiation.
Decisions are made based on the principle of "What's in it for me?"
"If I do what mom or dad wants me to do, they will reward me. Therefore I will do it.”
"you scratch my back, and I'll scratch yours."
Pre-conventional Moral
Reasoning
Pre-conventional Moral Reasoning
Stage 3
Social Conformity Orientation
By adolescence, most individuals have developed to this stage.
There is a sense of what
"good boys" and "nice girls" do and the emphasis is on living up to social expectations and norms because of how they impact day-to-day relationships.
“I want to be liked and thought well of; apparently, not being naughty makes people like me.”
Stage 4
Law and Order Orientation
By the time individuals reach adulthood, they usually consider society as a whole when making judgments.
The focus is on maintaining law and order by following the rules, doing one's duty and respecting authority.
Conventional moral reasoning
Conventional moral reasoning
Stage 5
Social Contract Orientation
At this stage, people understand that there are differing opinions out there on what is right and wrong and that laws are really just a social contract based on majority decision and inevitable compromise.
People at this stage sometimes disobey rules if they find them to be inconsistent with their personal values and will also argue for certain laws to be changed if they are no longer "working".
Our modern democracies are based on this reasoning.
Stage 6
Universal Ethics Orientation
Few people operate at this stage all the time.
It is based on abstract reasoning and the ability to put oneself in other people's shoes.
People have a principled conscience and will follow universal ethical principles regardless of what the official laws and rules are.
Post-Conventional Morality
Post-Conventional Morality
Lawrence Kohlberg
(October 25, 1927 – January 19, 1987)
Professor at The University of Chicago &
Harvard University
Having specialized in research on moral education and reasoning, he is best known for his theory of stages of moral development.
Created a new field within psychology:
"moral development".
Kohlberg was found to be the 30th most eminent psychologist of the 20th century.
[1]
Erik Erikson
(15 June 1902 – 12 May 1994)
Known for his theory on social development of human beings.
He may be most famous for coining the phrase identity crisis.
Although Erikson lacked even a bachelor's degree, he served as a professor of prominent institutions such as Harvard and Yale.
Age Virtues infant -18 months Hopes
18 month-3 years Will
3-5 years
5-13 years
13-21years
21-40 years
41-65 years
Purpose
Competence
Fidelity
Love
Care
Psycho
Social Crisis
Significant
Relationship
Existential
Question
Examples
Trust vs. Mistrust
Autonomy vs.
Shame & Doubt
Initiative vs. Guilt
Industry vs.
Inferiority
Identity vs. Role
Confusion
Intimacy vs.
Isolation
Generativity vs.
Stagnation
Ego Integrity vs.
Mother
Parents
Family
Can I Trust The
World?
Feeding,
Abandonment
Is It Ok To Be Me?
Toilet Training,
Clothing
Themselves
Is It Ok For Me To
Do, Move and
Act?
Exploring, Using
Tools or Making
Art
Neighbors, School
Can I Make It In
The World Of
People And
Things?
School, Sports
Peers, Role Model
Who Am I? What
Can I Be?
Social
Relationships
Friends, Partners Can I Love?
Romantic
Relationships
Household,
Workmates
Can I Make My
Life Count?
Is It Ok To Have
Work, Parenthood
Sources
http://www.usefulcharts.com/index.html
Thinking About Psychology The Science of
Mid and Behavior (Second Edition) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lawrence_Ko hlberg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Erikson%27s_ stages_of_psychosocial_development