8 - Images
advertisement
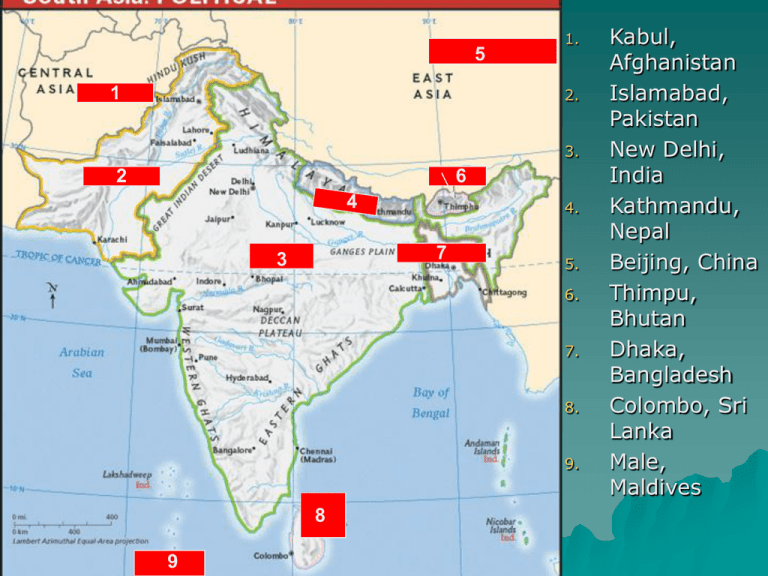
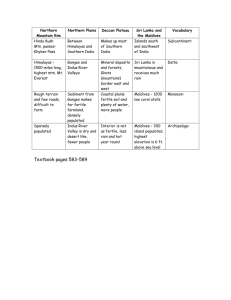
5 1. 2. 1 3. 2 6 4 4. 7 3 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 8 9 Kabul, Afghanistan Islamabad, Pakistan New Delhi, India Kathmandu, Nepal Beijing, China Thimpu, Bhutan Dhaka, Bangladesh Colombo, Sri Lanka Male, Maldives 5 1 2 4 6 7 3 8 9 Kabul, Afghanistan Islamabad, Pakistan New Delhi, India Kathmandu, Nepal Beijing, China Thimpu, Bhutan Dhaka, Bangladesh Male, Maldives Colombo, Sri Lanka Ch. 23: The Physical Geography of South Asia 23-1 Notes: The Land A Separate Land S. Asia=1/2 the size of the cont. U.S. India = 1/3 the size of the U.S. (but more than 3x the population!) S. Asia is a peninsula surrounded by the Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal, and the Indian Ocean. India is a subcontinent Sri Lanka & other islands are part of South Asia The Himalayas The Himalayas Indian subcontinent was part of Africa and drifted and smashed into Asia. Collision created the Himalayas Mt. Everest29,035 ft. (world’s tallest) is part of the Himalayas More on Everest…… Number of people to attempt to 1924 — British explorers George Mallory and Andrew climb Mt. Everest: Irvine disappear near the approximately 4,000. summit, along the Northeast Ridge. It is possible that they Number of people to may have actually been the successfully climb Mt. first to reach the summit, but Everest: 660. they never returned. 1949 — Nepal opens its Number of people who have borders, making access to the died trying to climb Mt. mountain's southern peak Everest: 142. possible 1953 — Hillary and Norgay Height: 29,035 feet, or 5 and reach summit a half miles above sea level. This is equivalent to the size 1963 — First Americans reach the summit of almost 20 Empire State 1989 — First two women, both Buildings. American, reach the summit. 1996 — Eleven people die during spring expeditions. Sir Edmund Hillary 1st to climb Everest Assisted by Sherpa Tenzing Norgay 1953 Other Northern Landforms Himalayas, Karakoram, & Hindu Kush form barrier between the subcontinent and the rest of Asia Khyber Pass Ganges Plain—at the foot of the Himalayas1/10 of the world’s population 3 rivers water the plain: Indus, Ganges, & Brahmaputra Central & Southern Landforms Vindhya Range divides India into Northern & Southern regions Southern Indiaeroded mtns. Eastern & Western Ghats Forms a triangle with the Deccan Plateau Rich soil, but arid (leeward effect) Maldivescoral atoll islands (coral developed on top of submerged volcano) Sri Lankawas once part of India, broke away from subcontinent The development of a coral atoll island: Indus & Brahmaputra Rivers Indus River Flows through Pakistan “cradle” of ancient India Supplied world’s earliest civilizations Brahmaputra River Flows east through the Himalayas & then west into Bangladesh Merges with Ganges R. Major waterway Ganges River S. Asia’s most important river Source in the Himalayas (does not dry up during dry season) Floods during rainy season Hindus consider it sacred “Mythically pure” Extremely polluted World’s largest alluvial plain India’s most densely populated area Natural Resources Water: Hydroelectric power; transportation S. Asia has some oil/nat. gas Uses imported oil Becoming more dependent on nuclear sources Ch. 23: The Physical Geography of South Asia 23-2 Notes: Climate & Vegetation South Asia’s Climates Much of India is south of the Tropic of Cancer & has a tropical climate Northern & Western climates vary from highlands to desert Tropical & Subtropical Climates West coast of India, Ganges Delta, & southern Sri Lanka=tropical rainforest climates – Seasonal rains from the southwest bring much rain to this area The central Indian steppe & eastern Sri Lanka have a tropical savanna climate (wet & dry seasons, grasslands, & deciduous forests) Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, NE India have a humid subtropical climate Highlands Climate The coldest areas of South Asia are on the northern edges Snow never melts in the Himalayan highlands Forests on the lower slopes Grasslands & bamboo are found in the foothills Dry Climates Dry climates are found along the lower Indus River The Great Indian Desert & steppe areas are found here; most of this area is wasteland Monsoons South Asia has 3 main seasons—hot, cool, & wet—that depend on the seasonal monsoons (winds) – Hot (late Feb.-June) warm temperatures—brings dry air – Wet (June-Sept.) Moist ocean air comes from the south & SW with monsoon rains – Cool (Oct-Late Feb) dry monsoons winds blow from the north & NW Monsoon Rains Heaviest in eastern South Asia When rain blows over the Ganges delta, the Himalayas block them from moving north. Rain then falls on the Ganges Plain Natural Disasters The high temperatures of the hot season are good & bad Extremely high temps & lack of rain can dry out the soil, causing droughts Too much rain caused by monsoons brings floods & can cause great damage & mudslides Cyclones—(like a hurricane) high winds, heavy rains, & tidal waves Tsunamis—huge wage caused by an underwater earthquake (can happen anytime of year) Ch. 24: The Cultural Geography of South Asia 24-1 Notes: Population Patterns Human Characteristics Over 1.3 billion people live in S.Asia >1/5 of the world’s population Speak hundreds of languages Practice several major religions Many Indians identify themselves by their religions as Hindus, Muslims, Buddhists, Sikhs, Jains, or Christians Others identify with their jati— a group that defines their occupation & social position India Pakistan & Bangladesh They were once part of British India Most practice Islam Later became separate countries Most people in Bangladesh are Bengali Sri Lanka’s Sinhalese & Tamils The Buddhist Sinhalese are the majority & control the gov’t Hindu Tamils have been fighting for an independent state in northern Sri Lanka since the 1980’s Thousands of deaths, disrupted economy, many refugees The Bhote & Tibetan people of Bhutan & the various ethnic groups of Nepal are descended from the Mongolians Most familiar group to outsiders— Sherpas—are known for their mountaineering skills A sherpa (Tenzing Norgay) made the first successful ascent of Everest with Sir Edmund Hillary in 1953. Bhutan & Nepal Population Density & Distribution 780 people/sq. mile= 7 times the world avg. At present rates, South Asia will nearly double its current population by 2050. Educational & economic improvements are helping to slow the rate Regional Variations Most people in the region live in agricultural areas, like the Ganges Plain or on the coasts (>2,000 ppl/sq mi) The tiny Maldives have 2,495 ppl/sq mi— making it the world’s most crowded country Desert & mtn areas in western Pakistan are thinly populated Bangladesh Slows Its Growth 2nd most populous country in S. Asia Trouble feeding its population Programs have encouraged women to have fewer children & get involved in business Number of children per woman decreased from 4 to 2.8 in the 1990’s Urban & Rural Life Most of S. Asia’s population is rural Pakistan, most urbanized, but 2/3 rural Rural Life Rural life has changed little Farming, villages, struggles to grow enough crops Nomadic groups that heard camels & goats Growing Urbanization Many S. Asians have moved to cities (better jobs) Overpopulation— shortages in housing, health care, education, & serious pollution South Asia’s Cities S. Asian cities are among the world’s most densely populated urban areas Mumbai (Bombay), a major port city on the Arabian Sea, is India’s largest with >18 million ppl Kolkata (Calcutta) is a major port city on the Ganges 5 of the world’s 13 largest cities are in South Asia 9 1 8 2 4 5 7 3 South Asia Map Quiz 6 Write the capital and country name for each number. 9 South Asia Map Quiz 1 8 2 3 Write the capital and country name for each number. 4 +2 each for naming capitals of countries with squares. 5 7 6 8 South Asia Map Quiz 7 9 6 1 Write the capital and country name for each number. 2 +2 each for naming capitals of countries with squares. 5 4 3 Today’s assignment: Answer all the “Map Study”, “Graph Study” and picture caption questions from pg561-578 561 (2), 563 (2), 571 (2), 572 (1), 573 (1), 574 (1), 576 (2), 577 (2), 578 (2) 15 questions You do not have to write the questions.