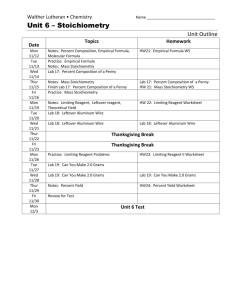
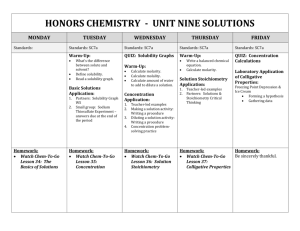
February 2014 Honors Chemistry –Perkerson
advertisement
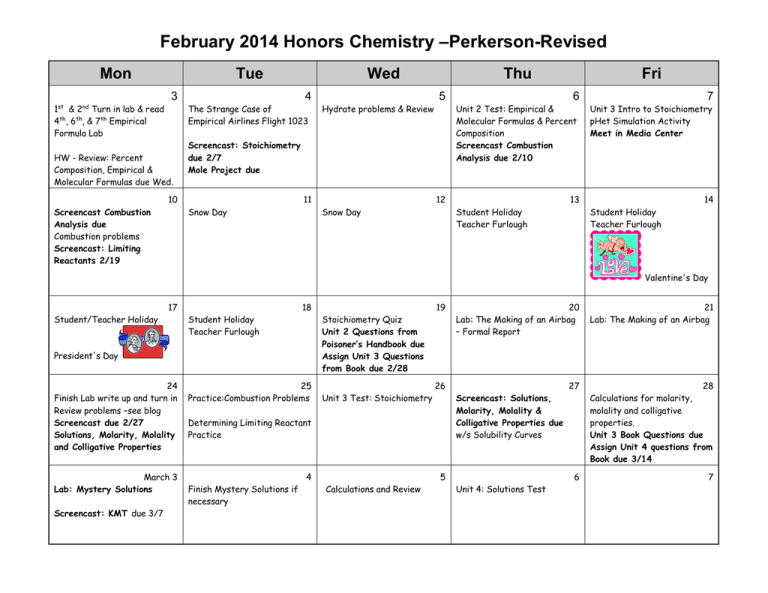
February 2014 Honors Chemistry –Perkerson-Revised Mon Tue 3 1st & 2nd Turn in lab & read 4th, 6th, & 7th Empirical Formula Lab Wed 4 The Strange Case of Empirical Airlines Flight 1023 HW - Review: Percent Composition, Empirical & Molecular Formulas due Wed. 5 Hydrate problems & Review Screencast: Stoichiometry due 2/7 Mole Project due 10 Screencast Combustion Analysis due Combustion problems Screencast: Limiting Reactants 2/19 Thu 11 Snow Day 6 7 Unit 2 Test: Empirical & Molecular Formulas & Percent Composition Screencast Combustion Analysis due 2/10 Unit 3 Intro to Stoichiometry pHet Simulation Activity Meet in Media Center 12 Snow Day Fri 13 Student Holiday Teacher Furlough 14 Student Holiday Teacher Furlough Valentine's Day 17 Student/Teacher Holiday 18 Student Holiday Teacher Furlough President's Day 24 Finish Lab write up and turn in Review problems –see blog Screencast due 2/27 Solutions, Molarity, Molality and Colligative Properties 25 Practice:Combustion Problems March 3 Lab: Mystery Solutions 4 Screencast: KMT due 3/7 19 Stoichiometry Quiz Unit 2 Questions from Poisoner’s Handbook due Assign Unit 3 Questions from Book due 2/28 Unit 3 Test: Stoichiometry 26 Determining Limiting Reactant Practice Finish Mystery Solutions if necessary 20 Lab: The Making of an Airbag – Formal Report 21 Lab: The Making of an Airbag 27 28 Calculations for molarity, molality and colligative properties. Unit 3 Book Questions due Assign Unit 4 questions from Book due 3/14 6 7 Screencast: Solutions, Molarity, Molality & Colligative Properties due w/s Solubility Curves 5 Calculations and Review Unit 4: Solutions Test *NOTE: It is expected that students will read appropriate chapters in the textbook without specific assignments being made. HW = homework, CW= class work, L & D = lecture and discussion PP = practice problems SR = section review W/S = worksheet Pre-lab must be completed BEFORE coming to class or student will not be allowed to participate in lab during class. SC2 Students will relate how the Law of Conservation of Matter is used to determine chemical composition in compounds and chemical reactions. c. Apply concepts of the mole and Avogadro’s number to conceptualize and calculate • Empirical/molecular formulas, • Mass, moles and molecules relationships, d. Identify and solve different types of stoichiometry problems, specifically relating mass to moles and mass to mass. e. Demonstrate the conceptual principle of limiting reactants. SC5. Students will understand that the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs can be affected by changing concentration, temperature, or pressure and the addition of a catalyst. a. Demonstrate the effects of changing concentration, temperature, and pressure on chemical reactions. b. Investigate the effects of a catalyst on chemical reactions and apply it to everyday examples. c. Explain the role of activation energy and degree of randomness in chemical reactions. Unit 4 Vocab: mole ratio stoichiometry Unit 5 Vocabulary solution molarity solute unsaturated dilute aqueous limiting reactant(reagent) molality saturated miscible percent yield colligative properties supersaturated immiscible solvent concentrated theoretical yield