TYPES OF HYBRIDIZATION AND GEOMETRY OF MOLECULES
advertisement

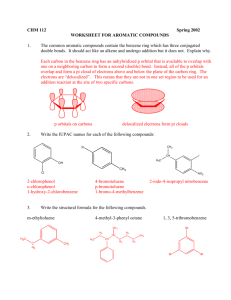
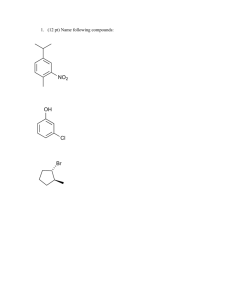
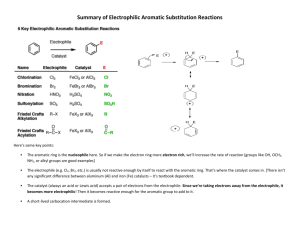
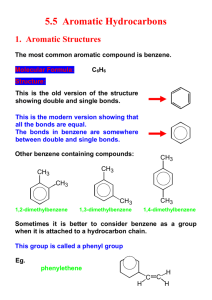
Aromatic compounds 1435-1436 2014-2015 Aromatic compounds Learning Objectives By the end of chapter four the students will: Understand the resonance description of structure of benzene Understand the hybridization in benzene Understand the relation between the stability of benzene and resonance energy Know the criteria of aromaticity and Huckel rule Understand the nomenclature rules of aromatic compounds and know the Common names of some aromatic compounds Understand the reactivity of aromatic compounds, know what are electrophiles and know the four types of electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions (halogenation, Freidel Crafts alkylation and acylation, nitration and Sulfonation). Know the reactions of alkyl side chains of aromatic compounds (halogenation, oxidation) Understand the orientation and reactivity of E.A.S reactions in monosubstituted benzene derivatives. Aromatic compounds Benzene : Resonance Description Primary analysis revealed benzene had... a molecular mass of 78 a molecular formula of C6H6 Structure: Kekulé suggested that benzene was... PLANAR CYCLIC Had Alternating Double And Single Bonds Thus These Double Bonds Are Described As Conjugated Bonds. Aromatic compounds However, all bond lengths in benzene to be equal and intermediate between single bond and double bond lengths (1.39 Å) and the ring is more stable than expected. To explain the above, it was suggested that the structure oscillated between the two Kekulé forms but was represented by neither of them. It was a RESONANCE HYBRID ( average of two structures that differ only in the placement of the valence electrons). Contributing Structures 4 The energy calculated for a resonance hybrid is lower than the energies of the two alternative structure. Resonance hybride Aromatic compounds 6 single bonds 5 one way to overlap adjacent p orbitals another possibility delocalised pi orbital system Aromatic compounds Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds * electron cloud delocalized all over the ring * The resonance picture this helps to explain lack of reactivity of benzene (substitution not addition ) Aromatic compounds are compounds that resemble benzene in chemical behavior thus they tend to react by substitution rather than by addition and fulfill the aromaticity requirements. 6 Aromatic compounds Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds To be classified as aromatic, a compound must have : 1) Cyclic structure. 2) Planar structure. 3) Each atom of the ring must have a p orbital to form a delocalized π system i.e. no atoms in the ring can be sp3 hybridized instead all atoms must be sp2 hybridized (N.B. carbocation and carbanions are sp2 hybridized or an unshared pair electrons). 4) Fulfill Huckel rule i.e. the system must have 4n + 2 pi electrons : thus by calculating n value it will be an integral number i.e. n=0, 1, 2, 3, Aromatic compounds Examples of aromatic compounds O N N H 4n+2=6 n=1 4n+2=6 n=1 4n+2=6 n=1 4n+2=6 n=1 4n+2=6 n=1 N H 4n+2=2 n=0 4n+2=10 n=2 4n+2=10 n=2 4n+2=6 n=1 Aromatic compounds Examples of non aromatic compounds carbon indicted by n=1/2 n=1/2 is sp 3 n=1/2 4n+2=8 n=1.5 9 Aromatic compounds Nomenclature of Aromatic Compounds 1. Monosubstituted Benzenes a. IUPAC Names They are named as derivatives of benzene. One side group is named as a prefix in front of the word benzene. No number is needed for mono-substituted benzene. C(CH3)3 tert-Butyl-benzene CH2CH3 Ethyl-benzene NO2 Nitro-benzene Cl Chloro-benzene Aromatic compounds Benzene ring has priority over :side chains with alkyl, alkoxy groups, halogens, double and triple bonds C CH Vinyl-benzene Allyl-benzene Ethynyl-benzene OCH3 Butyl-benzene Methoxy-benzene In some cases the side chains on aromatic ring contain functional groups of higher priorities (NH2, OH, CHO,C=O, COOH, COOR) thus in this case the aromatic ring will be considered as a substituent and the side chain will be used to give the root name. Two aromatic radials are known CH2 11 Benzyl group phenyl group (C6H5-) Aromatic compounds Any aryl group (Ar) is the aromatic group that remains after removal of hydrogen Atom from an aromatic ring. When the benzene ring is named as substituent, it is called a phenyl group (often abbreviated Ph). A benzyl group (the phenyl methyl group) is the seven carbon unit consisting of benzene ring and methylene (-CH2-). b. Common Names Of Monosubstituted Benzenes CH3 Toluene CH=CH2 Styrene OH Phenol H O Benzaldehyde HO O Benzoic acid NH2 Aniline OCH3 Anisol Aromatic compounds A hydrocarbon composed of one saturated chain and one benzene ring is usually named as a derivative of the larger structural unit. However, if the chain is unsaturated compound may be named as a derivative of that chain, regardless of ring size. The following are examples: 13 Aromatic compounds 2. Nomenclature of Disubstituted and polysubstituted Benzenes All disubstituted benzenes (two groups are attached to benzene), can give rise to three possible positional isomers. X X X Y Y Y Common: orthIUPAC: 1,2- meta 1,3- para 1,4- When the substituents are different, they are of equal priorities they will should be listed in alphabetical order. C2H5 NO2 Cl I Common: IUPAC: o-Chloroethylbenzene 1-Chloro-2-ethylbenzene Br m-Bromonitrobenzene 1-Bromo-3-nitrobenzene F p-Fluoroiodobenzene 1-Fluoro-4-iodobenzene Aromatic compounds CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 Common: IUPAC: o-Xylene 1,2-Dimethyl-benzene m-Xylen 1,3-Dimethyl-benzene p-Xylene 1,4-Dimethyl-benzene If one of the substituents is part of a parent compound, then the disubstituted or polysubstituted benzene is named as a derivative of that parent compound i.e. priorities determine the root name and substituents. OH COOH NO2 Cl CHO CH3 OCH3 NO2 O 2N NO2 Br CH3 Common: o- Chlorophenol IUPAC: 2-Chlorophenol m-Bromobenzoic acid 3-Bromobenzoic acid p-Nitrotoluene 4-Nitrotoluene o-Methoxybezaldehyde 2-Methoxybezaldehyde 2,4,6- Trinitrotoluene Aromatic compounds Reactions Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions COR RCOCl, AlCl3 Acylation Aromatic compounds acetophenone 17 Aromatic compounds Side-Chain Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 1)Halogenation a. Halogenation of an Alkyl Side Chain CH3 CH 2Br Br2 + UV light Toluene HBr Benzyl Bromide CHClCH3 CH2CH3 CH2CH2Cl Cl2/ UV Major Minor 18 Aromatic compounds b. Oxidation of an Alkyl Side Chain CH3 COOH - KMnO 4, OH , H2O, heat H3O + Toluene Benzoic acid CH3 COOH CH2CH3 KMnO 4, OH , H2O, heat H3O NO 2 COOH + + CO 2 + H2O NO 2 19 Aromatic compounds Orientation effects of substituents in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions of monosubstituted Benzenes Alkyl groups and groups with lone pairs (electron donating groups) direct new groups to ortho, para-positions and speed-up the reaction (i.e. o & p directors and activating groups). Halogens direct new groups to ortho-, para- positions but they slow down the reaction (i.e. halogens are o & p directors and deactivating groups). Electron withdrawing groups such as nitro, nitrile, and carbonyl direct new groups to the meta-position and slow the reaction down (i.e. i.e. m directors and deactivating groups). Thus the order of reactivity of benzene and monosubstituted benzene derivatives in E.Ar.sub. is as in the following chart Substituted benzene with o,p directors > Benzene > Halobenzene derivatives > Substituted benzene with m- directors Aromatic compounds Orientation effects of substituents in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions of monosubstituted Benzenes Ortho , para directors Meta directors -OH, -OR -NH2, -NHR, -NR2 -C6H5 -CH3, -R (alkyl) -F, -Cl, -Br, -I -NO2 -SO3H -COOH, -COOR -CHO, -COR -CN OH OH OH NO2 HNO3 / H2SO4 + o-Nitrophenol 53 % NO2 NO2 NO2 p-Nitrophenol 47 % SO3 / H2SO4 SO3H m-Nitrobezenesulfonic acid Aromatic compounds 22 Aromatic compounds Q1: What are the major products of the following reaction? Q2: What is the empirical formula of the following compound: (pmethyl-Toluene): a) C8H10 b) C8H12 c) C8H14 d) C6H14 Aromatic compounds Q3: What is the final product of the following reaction? a) o-chlorobenzaldehyde b) m-chlorobenzaldehyde c) p-chlorobenzaldehyde d) a,c Q4:Which one of the following compounds has aromatic character? 24 Aromatic compounds Thank You for your kind attention ! Questions? Comments 25