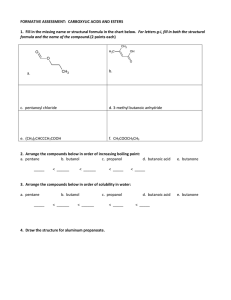
What is an ALCOHOL
advertisement

Alcohol Family I W E N Beer Rubbing Alcohol “Are you one of those people having a wrong perception regarding the NATURE and APPLICATION of organic compound, ALCOHOL?” Alcoholic beverages and rubbing alcohol are examples of numerous industrial applications of an alcohol called ………….. ETHANOL AMAZING HISTORY OF ALCOHOL OSIRIS EGYPTIANS Brewing from the beginning of civilization in ancient Egypt and alcoholic beverages were very important. Symbolic of this is the fact that while many Gods were local or familial, Osiris, the god of wine, was worshiped throughout the entire country. The Egyptians believed that this important God also invented beer, a beverage that was considered a necessity of life; it was brewed in the home "on an everyday basis." CHINESE A variety of alcoholic beverages were used in China since prehistoric times. Alcohol, known in Chinese as Jiu was considered a spiritual food rather than a material (physical) food, and extensive documentary evidence attests to the important role it played in the religious life. "In ancient times people always drank when holding a memorial ceremony, offering sacrifices to gods or their ancestors, pledging resolution before going into battle, celebrating victory, before feuding and official executions, for taking an oath of allegiance, while attending the ceremonies of birth, marriage, reunions, departures, death, and festival banquets." MUSLIMS The isolation of ethanol (alcohol) as a pure compound was first achieved by Muslim chemists who developed the art of distillation The word "alcohol" almost certainly comes from Arabic language "Al" is Arabic word second part may be derived from “al-kuḥl” the name of an early distilled substance, or perhaps from al-ġawl, meaning "spirit" or "demon“ being called "spirits" in English. But ………………………….. the reality, is that there are thousands of different compounds that belong to “Alcohol Family”. METHANOL 2 - PROPANOL tert - butanol Ethylene glycol glycerin MENTHOL Now the BIG question is ……… What is an ALCOHOL ? • Is a compound in which an (OH) group or hydroxyl group is connected to an aliphatic carbon atom. PHYSICAL Properties ALCOHOL Is a derivative of water in which an ALKYL group has replaced one of the hydrogen atoms of water or simply ALCOHOL exhibits hydrogen bonding…………………. O H H Water O CH3 H Methanol That property or ………. HYDROGEN BONDING results to much point higher boiling of ALCOHOL compares to other classes of organic compounds………………. ALCOHOL’S with one to five carbon atoms are soluble in water because alcohols can also form hydrogen bonding with water. But as the number of carbon atoms increases , the polar – (OH) group in the alcohol has less effect on SOLUBILITY of ALCOHOL ………………… NAME FORMULA S – (g / 100 g H2O) Methanol CH3OH Any amount Ethanol CH3CH2OH Any amount Propanol CH3(CH2)2OH Any amount Butanol CH3(CH2)3OH 8.3 Pentanol CH3(CH2)4OH 2.7 How to produce ALCOHOL ? PREPARATION’S NOMENCLATURE methanol ethanol propanol 2 – propanol 2 methyl – 2 – propanol RULES IN NAMING ALCOHOL Step # 1 Name the longest chain to which the hydroxyl group is attached. The chain name is obtained by dropping the final –e from the name of the hydrocarbon that contains the same number of carbon atoms and adding the ending – ol. 8 4 5 9 7 6 1 2 3 4,4,6,6 – tetraethyl – 5 – methyl – 5 – nonanol Step # 2 Number the longest chain to give the lower number to the carbon with the attached hydroxyl group. Step # 3 Locate the position of the hydroxyl group by the number of the carbon atom to which it is attached. Step # 4 Locate and name any other groups attached to the chain. Step # 5 Combine the name and location for other groups, the hydroxy group location, and the longest chain into the final name. cyclohexanol 1 - propenol 3 - pentynol 2,3 – dimethyl – 1 – hexen – 4 – yne – 1 – ol Classification of Alcohols Primary Alcohol An alcohol in which the – OH group is attached to CH3 – or to a carbon attached to one other carbon atom. R – CH2 – OH Secondary Alcohol An alcohol in which the carbon bearing the – OH group is attached to two other carbon atoms. R – CH – OH R’ Tertiary Alcohol An alcohol in which the carbon bearing the – OH group is attached to three other carbon atoms. R R’ C R” OH Chemical Reactions Elimination Reactions Oxidation Dehydration