Iran Presentation 3 Citizens Society and the State
advertisement

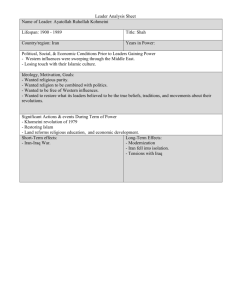
The Islamic Republic of Iran Citizens, Society & The State Presentation Outline III. Citizens, Society, & The State a) Political socialization b) Cleavages c) Civil society and interest groups d) Protest and demonstrations III. a) Political Socialization 1) 2) 3) 4) Family Public Schools University campuses Basij and Revolutionary Guard Family The Family plays a major role in political socialization. Children who grow up in more secular (non-religious) homes tend to have more liberal and democratic values while children who grow up in more religious families tend to support the regime’s theocratic policies. The picture on the left tells the tale of two families (one secular/ one religious) Public Schools • In Iran females and males are segregated and attend separate schools • Pictures of Ayatollah Khomeini, leader of the revolution, are present in every classroom and students are instructed to learn Iran’s revolutionary songs, praise Khomeini, and fight for and believe in Iran’s theocracy Left are female primary students honoring Khomeini and giving thanks for the revolution on the anniversary of Iran’s Revolution University Campuses • Iran has a large population under the age of 30 • Campuses are generally a hotbed of student radicalism and protests • Since 1989 many of these protests have been directed against the regime with class for reform and democratization Basij and Revolutionary Guard The Basij (voluntary militia) and the Revolutionary Guard (full-time army which protects the Supreme Leader) are ultranationalist and conservative elements which strong support the regime The Basij The Revolutionary Guard III. b) Cleavages 1) Ethnicity 2) Religion 3) Secular vs. Religious Ethnicity • Iran is a multi-ethnic state with Persians constituting about 51% of the population • Among the larger ethnic minorities are Azeris, Kurds, and Arabs • Although Iran has NOT experienced separatism many ethnic minorities have expressed dissatisfaction with the Persian majority Ethno- Religious Groups in Iran 90% of Iranians are Shi’a Muslims Shi’a Islam is a cross-cutting cleavage which ensures stability. Ethnic Groups Influence/Power Religion Wealth Persians Well-represented in power and politics Shi’a Islam Poor/middle class/wealthy Azeris Well-represented in power and politics Shi’a Islam Poor/middle class/wealthy Kurds Underrepresented in power and politics Shi’a Islam Mostly poor and middle class Arabs Underrepresented in power and politics Shi’a Islam Mostly poor and middle class Secular vs. Religious cleavage • The most significant cleavage is the divide between the ultra-religious and the nonreligious or secular middle classes • Generally, secular Iranians tend to support reformist politicians and democratization while the ultra-religious tend to strongly support conservative politicians and the regime. One State but Two Different Worlds and Visions! III. c) Civil Society and Interest groups • Iran civil society exists but is highly restricted by the regime • Interest groups which criticize Shi’a Islam or the regime tend to be crushed very quickly Iran’s press • Iran has both private and public media • The media, however, is forbidden from criticizing the regime, the Supreme Leader, or Shi’a Islam • The media may comment on the economy, the Majles, and the president and even offer criticisms • Foreign media and the internet is heavily censored Freedom House rates Iran’s Press as Not Free Internet Censorship and Filtering: The darkest color represents states with the highest level of censorship. Any familiar places? Interest groups Iran does not have an organized system of interest groups Informally, the bazaari merchants have had a lot of influence over economic policy over the last 20 years The bazaari merchants are well-organized and control about one third of Iran’s retail sales. They sell spices, clothes, furniture, and rugs among many other items. In the past, Iranian governments have given them generous subsidies on fuel to run their businesses. At times, they have even gone on strike to force their demands. III. d) Protests and demonstrations • The regime does not encourage protests and demonstrations unless they are directed against the United States or Israel. Does this sound familiar? • Demonstrations for reform and democratization have occurred since 1989 and have been largely supported by young Iranians, particularly university students • The two major protest events occurred in 1999 and 2009 1999 Student Protest In early July, 1999 thousands of university students peacefully demonstrated on the streets of Tehran to protest the government’s closing of a reformist newspaper. The government sent in the Basij to crush the protests. Approximately 10 people died and over a thousand were arrested. Iconic photo of a demonstrator holding up the shirt of his friend who had been killed by the Basij. 2009 Protests Tens of thousands of Iranians, many of them under 30 years old, took to the streets of Tehran, and other major cities in Iran to protest the result of the 2009 presidential election. Many claimed that the election was fraudulent and that Mir Hossein Mousavi had been denied the presidency by the Basij and Guardian Council The Green Revolution: Reformists chose Green as the color of revolution and democracy. The Supreme Leader responded by sending in the Basij to crush the demonstrations.