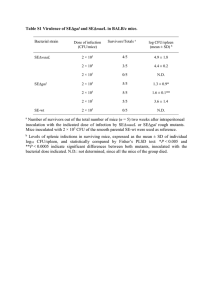
Characteristics of Life
advertisement

What is Science • SCIENCE: Is using evidence to learn about the natural world • The Goal of Science 1.) Deals only with the natural world 2.) To collect and organize data 3.) Propose explanations that can be tested What is Biology? • Biology • (bio = life and –ology = The study of) • Biology = The study of life! Scientific Method • “One of the best ways to begin science is to examine how scientist try to solve problems or answer questions” Observing & Asking Questions • Science ALWAYS begins by observing and asking questions • Example: Do plants with more light grow better than plants with less light? • Other Possible Questions? Hypothesizing • Hypothesis- is a statement that both explains your observations and data and must be testable • Create an “if-then” Prediction • IF the plants receive more light THEN they will grow larger. Experimenting • Most experiments are controlled experiments • Parts to a controlled experiment – Controlled group (standard or normal) – Experimental group – Independent variable (one factor you change) – Control Variable (factors we keep the same) – Dependent variable (depends on the independent Variable) Control Group • Control Group: The normal or the group that we compare our experimental group to. (example: The normal plant that is by the normal amount of light) Control Variables • Variable that do not change in an experiment • Examples – Soil – Pots – Plants – Amount of Water Independent Variable • The Variable you change • The amount of light the plants receive • Placed on the X axis on a graph Dependent Variable • The Variable that is measured (Depends on the independent Variable) • The height of the plants • Placed on the Y axis on a graph Collecting Data • Longest phase of a scientific investigation. • Data includes any and all information that scientist gather in trying to answer their question. • All data must be measureable (metric system used in science) What is DATA • Two types of data – 1.) Quantitative data = NUMBERS – 2.) Qualitative data = DESCRIPTIVE WORDS Drawing Conclusions • Analyzing your data so that you can determine if your hypothesis was correct or incorrect. • Forming a theory. A theory is NOT a “wild guess” it is NOT a hypothesis, but rather a statement of what is thought to be true. • A theory is supported by evidence. What They Found • Plants with more light grew better than plants with less light Plants in Closet Plants near window Plants outside Try This Bart believes that mice exposed to radiowaves will become extra strong (maybe he's been reading too much Radioactive Man). He decides to perform this experiment by placing 10 mice near a radio for 5 hours. He compared these 10 mice to another 10 mice that had not been exposed. His test consisted of a heavy block of wood that blocked the mouse food. he found that 8 out of 10 of the radiowaved mice were able to push the block away. 7 out of 10 of the other mice were able to do the same. Identify the11. Control Group 12. Independent Variable 13. Dependent Variable 14. What should Bart's conclusion be?