PROTEIN SYNTHESIS NOTES
advertisement

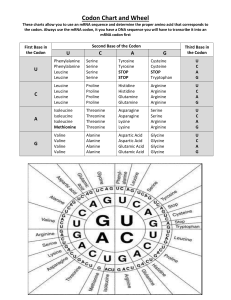
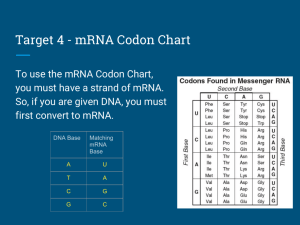
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS NOTES #1 Review What is transcription? Copying of DNA onto mRNA Where does transcription occur? In the Nucleus When copying DNA onto mRNA there is no Thymine (T) instead there is Uracil (U) A – U; G – C More Review What is Translation? The changing of mRNA into a protein Where does Translation occur? In the Ribosome What is a codon? 3 bases on mRNA What is an anticodon? 3 bases on tRNA Last of the Review What type of RNA carries the amino acids to the ribosomes? tRNA What is the start codon? AUG What are the stop codons? UGA, UAA and UAG Codon Wheel or Codon Chart Each codon (3 bases on mRNA) codes for a particular amino acid You find which amino acid is coded for by looking on one of the codon charts Codon Wheel – start from the middle and work your way out Codon Chart – Start on the left side, then the bottom (or top) and then the right side The Genetic Code (mRNA) A 1st Base in Codon G Lysine Lysine Asparagine Asparagine Arginine Arginine Serine Serine Isoleucine Methionine Isoleucine Isoleucine Threonine Threonine Threonine Threonine A G U C Glutamic acid Glutamic acid Glycine Glycine Glycine Glycine Valine Valine Valine Valine Alanine Alanine Alanine Alanine A G U C ‘Stop” codon Tyrosine Tyrosine Tryptophan Cysteine Cysteine Leucine Leucine Phenylalanine Phenylalanine Serine Serine Serine Serine A G U C Glutamine Glutamine Histidine Histidine Arginine Arginine Arginine Arginine Leucine Leucine Leucine Leucine Proline Proline Proline Proline A G U C A G U C Aspartic acid Aspartic acid “Stop” codon “Stop” codon U C 2nd Base in Codon 3rd Base in Codon Practice Using One of the Codon Charts If the codon is GCC, what is the amino acid? Alanine If the codon is UGG, what is the amino acid? Tryptophan If the codon is AGU, what is the amino acid? Serine More Practice Using One of the Codon Charts Can you go backwards? How many codons are there for the amino acid proline? 4 Name CCU, Name AGG, the 4 codons for proline. CCC, CCA, CCG 2 of the codons for arginine. AGA, CGG, CGA, CGC, CGU Protein Synthesis Practice If one side of the DNA strand is: TACACCGGTCCATTTACT What is the complementary (other) side of the DNA strand? ATGTGGCCAGGTAAATGA Protein Synthesis Practice Using the original DNA strand: TACACCGGTCCATTTACT Perform transcription – what is the mRNA produced? AUGUGGCCAGGUAAAUGA Protein Synthesis Practice Break the mRNA into codons (groups of 3): AUGUGGCCAGGUAAAUGA Perform Translation- what is the protein produced? Meth – Tryp – Pro – Gly – Lys (stop) (start) Another Protein Synthesis Practice Problem If DNA is: TACAATGCCAGTGGTTCGCACATT What is the mRNA? AUGUUACGGUCACCAAGCGUGUAA What is the protein made? Meth-Leu-Arg-Ser-Pro-Ser-Val (stop)