1-9 PPT
advertisement
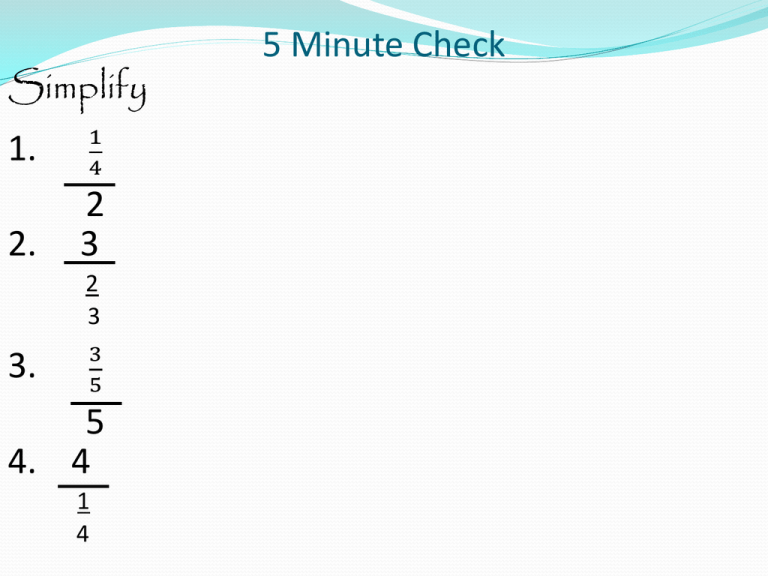
Simplify 1. 1 4 2. 2 3 2 3 3. 3 5 5 4. 4 1 4 5 Minute Check Simplify 1. 1 4 2 5 Minute Check 5 Minute Check Simplify 1. 1 4 2 1 ÷ 4 2 1 1 4 1 2 · = 1 8 Simplify 2. 3 2 3 5 Minute Check 5 Minute Check Simplify 2. 3 2 3 3 1 3 1 ÷ 2 3 · 3 2 = 9 2 1 2 =4 Simplify 3. 3 5 5 5 Minute Check 5 Minute Check Simplify 3 5 3. 5 3 5 3 5 ÷ 5 1 · 1 5 = 3 25 Simplify 4. 4 1 4 5 Minute Check 5 Minute Check Simplify 4. 4 1 4 4 1 1 4 ÷ 4 1 · 4 1 = 16 Friday, Jan 9 Lesson 7.1.3/7.1.4 Convert Unit Rates/ Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Convert Unit Rates Objective: To convert units of measure between derived units to solve problems. Convert Unit Rates The relationships among some commonly used customary and metric units are shown in the tables below. Convert Unit Rates Each of the relationships in the tables can be written as a unit ratio. A unit ratio, like a unit rate, has a denominator of one unit. Convert Unit Rates A remote control car travels at a rate of 10 feet per second. How many inches per second is this? How to Convert Unit Rates Step 1 – Write the complete rate as a fraction with units . Convert Unit Rates A remote control car travels at a rate of 10 feet per second. How many inches per second is this? 10 ft 1s How to Convert Unit Rates Step 1 – Write the complete rate as a fraction with units . Convert Unit Rates A remote control car travels at a rate of 10 feet per second. How many inches per second is this? 10 ft 1s How to Convert Unit Rates Step 2 – Determine the units of the answer and write as a fraction. Convert Unit Rates A remote control car travels at a rate of 10 feet per second. How many inches per second is this? 10 ft in Leave space for the 1s 1s = conversion rate. How to Convert Unit Rates Step 2 – Determine the units of the answer and write as a fraction. Convert Unit Rates A remote control car travels at a rate of 10 feet per second. How many inches per second is this? 10 ft in Leave space for the 1s 1s = conversion rate. How to Convert Unit Rates Step 3 – Determine the units of the conversion rate(s). Convert Unit Rates A remote control car travels at a rate of 10 feet per second. How many inches per second is this? conversion rate . 10 ft in in 1s ft 1s = How to Convert Unit Rates Step 3 – Determine the units of the conversion rate(s). Convert Unit Rates A remote control car travels at a rate of 10 feet per second. How many inches per second is this? conversion rate . 10 ft in in 1s ft 1s = The conversion rate units are determined by the original rate units and the answer units. In the above case, we need to cancel the “ft” units and replace with “in” units. Notice the conversion rate has “ft” in the denominator, so it will cancel the “ft” of the original rate. Convert Unit Rates A remote control car travels at a rate of 10 feet per second. How many inches per second is this? 10 ft in in 1s ft 1s = conversion rate. How to Convert Unit Rates Step 4 – Complete the conversion rate(s). Eg. How many inches in how many feet? Convert Unit Rates A remote control car travels at a rate of 10 feet per second. How many inches per second is this? 10 ft 12 in in 1s 1 ft 1s = conversion rate. How to Convert Unit Rates Step 4 – Complete the conversion rate(s). Convert Unit Rates A remote control car travels at a rate of 10 feet per second. How many inches per second is this? 10 ft 12 in in 1s 1 ft 1s = How to Convert Unit Rates Step 5 – Multiply and cancel units. Convert Unit Rates A remote control car travels at a rate of 10 feet per second. How many inches per second is this? 10 ft 12 in 120 in 1s 1 ft 1s = How to Convert Unit Rates Step 5 – Multiply and cancel units. Convert Unit Rates A swordfish can swim at a rate of 60 miles per hour. How many feet per hour is this? Step 1 - ? Convert Unit Rates A swordfish can swim at a rate of 60 miles per hour. How many feet per hour is this? 60 mile 1h Step 2 - ? Convert Unit Rates A swordfish can swim at a rate of 60 miles per hour. How many feet per hour is this? 60 mile 1h Step 3 – ? = ft 1h Convert Unit Rates A swordfish can swim at a rate of 60 miles per hour. How many feet per hour is this? 60 mile 1h ft mile = ft 1h Remember – we want to cancel the “mile” unit in the numerator of the original rate. In order to do so, the conversion rate must have a “mile” unit in the denominator. Step 4 – ? Convert Unit Rates A swordfish can swim at a rate of 60 miles per hour. How many feet per hour is this? 60 mile 1h 5280 ft 1 mile = ft 1h How many feet in how many miles? Step 5 – ? Convert Unit Rates A swordfish can swim at a rate of 60 miles per hour. How many feet per hour is this? 60 mile 1h 5280 ft 1 mile = 316, 800 ft 1h Convert Unit Rates A gull can fly at a speed of 22 miles per hour. How many feet per hour can the gull fly? Do this on your own. Convert Unit Rates A gull can fly at a speed of 22 miles per hour. How many feet per hour can the gull fly? 22 miles 1h 5280 ft 1 mile = 116,160 ft 1h Convert Unit Rates Marvin is walking at a speed of 7 feet per second. How many feet per hour is this? Do this on your own. Convert Unit Rates Marvin is walking at a speed of 7 feet per second. How many feet per hour is this? 7 ft 1s 420 ft 1 min 60 s 1 min = 60 min 1h 420 ft 1 min = 25,200 ft 1h Or you can create one large conversion rate… Convert Unit Rates Marvin is walking at a speed of 7 feet per second. How many feet per hour is this? 7 ft 1s 60 s · 60 min 1 min · 1 h = 25,200 ft 1h Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Objective: To identify and understand proportional and nonproportional relationships. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Two quantities are proportional if they have a constant ratio or rate. All of the ratios above are equivalent ratios because they all have the same value. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships For relationships in which the ratio is not constant, the two quantities are nonproportional. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Andrew earns $18 per hour for mowing lawns. Is the amount of money he earns proportional to the number of hours he spends mowing? Explain. How to Determine if a Rate or Ratio is Proportional. Step 1 – Make a table. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Andrew earns $18 per hour for mowing lawns. Is the amount of money he earns proportional to the number of hours he spends mowing? Explain. How to Determine if a Rate or Ratio is Proportional. Step 1 – Make a table. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Andrew earns $18 per hour for mowing lawns. Is the amount of money he earns proportional to the number of hours he spends mowing? Explain. How to Determine if a Rate or Ratio is Proportional. Step 2 – Simplify the rates or ratios. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Andrew earns $18 per hour for mowing lawns. Is the amount of money he earns proportional to the number of hours he spends mowing? Explain. How to Determine if a Rate or Ratio is Proportional. Step 2 – Simplify the rates or ratios. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Andrew earns $18 per hour for mowing lawns. Is the amount of money he earns proportional to the number of hours he spends mowing? Explain. How to Determine if a Rate or Ratio is Proportional. Step 2 – Simplify the rates or ratios. Since all rates can be simplified to 18, they are proportional. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Uptown Tickets charges $7 per baseball ticket plus a $3 processing fee per order. Is the cost of an order proportional to the number of tickets ordered? Explain. Step 1 - ? Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Uptown Tickets charges $7 per baseball ticket plus a $3 processing fee per order. Is the cost of an order proportional to the number of tickets ordered? Explain. Step 2 - ? (It doesn’t matter which unit is top or bottom) Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Uptown Tickets charges $7 per baseball ticket plus a $3 processing fee per order. Is the cost of an order proportional to the number of tickets ordered? Explain. Since all rates do not simplify to the same, they are nonproportional. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships You can use recipe shown to make fruit punch. Is the amount of sugar used proportional to the amount of mix used? Explain. Do this on your own. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships You can use recipe shown to make fruit punch. Is the amount of sugar used proportional to the amount of mix used? Explain. Since all rates can be simplified to 0.5, they are proportional. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships The tables shown represent the number of pages Martin and Gabriel read over time. Which situation represents a proportional relationship between the time spent reading and the number of pages read? Explain. Do this on your own. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships The tables shown represent the number of pages Martin and Gabriel read over time. Which situation represents a proportional relationship between the time spent reading and the number of pages read? Explain. Only Martin’s ratios can be simplified to the 3 5 same ( ). Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships The Vista Marina rents boats for $25 per hour. In addition to the rental fee, there is a $12 charge for fuel. Is the number of hours you rent the boat proportional to the total cost? Explain. Do this on your own. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships The Vista Marina rents boats for $25 per hour. In addition to the rental fee, there is a $12 charge for fuel. Is the number of hours you rent the boat proportional to the total cost? Explain. No, The cost to times ratios are not the same. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Which situation represents a proportional relationship between the number of laps run by each student and their time? Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Which situation represents a proportional relationship between the number of laps run by each student and their time? Desmond’s time is proportional. It takes him 73s for every lap. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Plant A is 18 inches tall after 1 week, 36 inches after 2 weeks, 56 inches after 3 weeks. Plant B is 18 inches tall after 1 week, 36 inches after 2 weeks, 54 inches after 3 weeks. Which represents a proportional relationship between the height and number of weeks? Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Plant A is 18 inches tall after 1 week, 36 inches after 2 weeks, 56 inches after 3 weeks. Plant B is 18 inches tall after 1 week, 36 inches after 2 weeks, 54 inches after 3 weeks. Which represents a proportional relationship between the height and number of weeks? Plant A Plant B Height 18 36 56 Height 18 36 54 Weeks 1 2 3 Weeks 1 2 3 Plant B grows at 18 inches per week. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Johanna’s parents give her $10 per week for lunch money. Blake ran laps around the gym. His times are shown in the table. Blake is trying to decide whether the number of laps is proportional to the time. Find his mistake and correct it. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Johanna’s parents give her $10 per week for lunch money. Blake ran laps around the gym. His times are shown in the table. Blake is trying to decide whether the number of laps is proportional to the time. Find his mistake and correct it. They are not proportional. The 1st min was 25 sec per lap, the 2nd min was 33 sec per lap. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Johanna’s parents give her $10 per week for lunch money. True or false? If a function rule has only multiplication and/or division it is a proportional relationship. Give examples to support your answer. Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Johanna’s parents give her $10 per week for lunch money. True or false? If a function rule has only multiplication and/or division it is a proportional relationship. Give examples to support your answer. If a simplified function rule has only multiplication and/or division it is a proportional relationship. Proportional Nonproportional x 1 2 3 3x 3 6 9 x 3x +2 1 5 2 8 3 11 Proportional and Nonproportional Relationships Agenda Notes Complete the Mid-Chapter Check on page 44 and bring to my desk. Homework – Homework Practice 7.1.3 and 7.1.4 Due Mon, Jan 12 Mid-Chapter 7.1 Quiz - Monday, Jan 12