Muscular System - Powell County Schools
advertisement
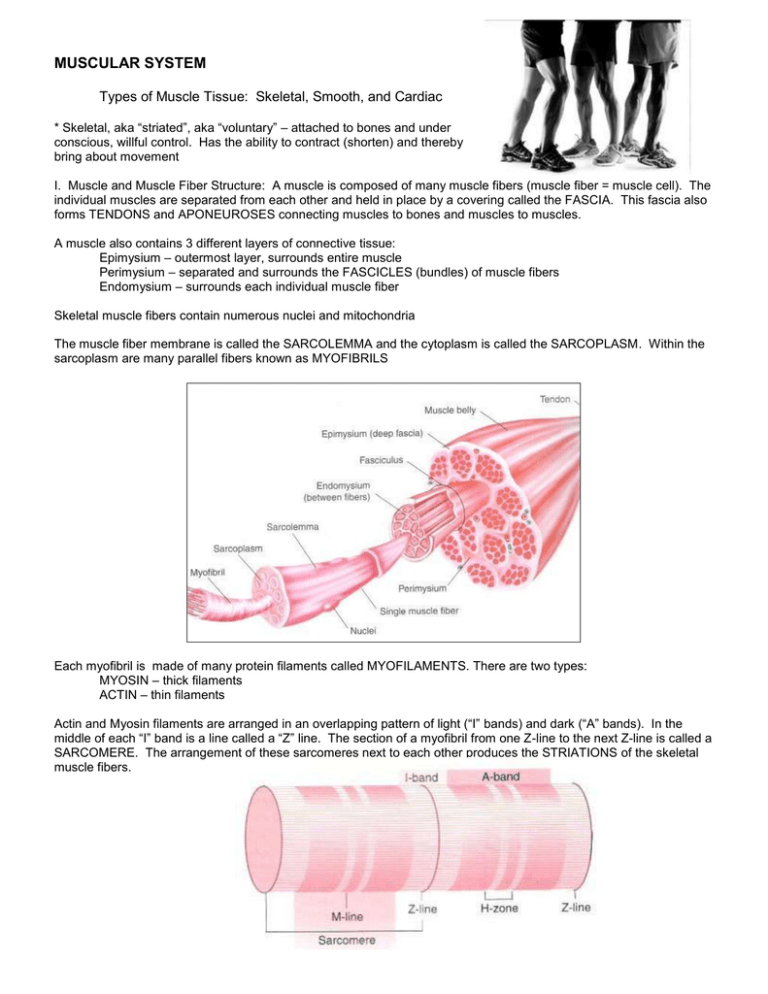
MUSCULAR SYSTEM Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal, Smooth, and Cardiac * Skeletal, aka “striated”, aka “voluntary” – attached to bones and under conscious, willful control. Has the ability to contract (shorten) and thereby bring about movement I. Muscle and Muscle Fiber Structure: A muscle is composed of many muscle fibers (muscle fiber = muscle cell). The individual muscles are separated from each other and held in place by a covering called the FASCIA. This fascia also forms TENDONS and APONEUROSES connecting muscles to bones and muscles to muscles. A muscle also contains 3 different layers of connective tissue: Epimysium – outermost layer, surrounds entire muscle Perimysium – separated and surrounds the FASCICLES (bundles) of muscle fibers Endomysium – surrounds each individual muscle fiber Skeletal muscle fibers contain numerous nuclei and mitochondria The muscle fiber membrane is called the SARCOLEMMA and the cytoplasm is called the SARCOPLASM. Within the sarcoplasm are many parallel fibers known as MYOFIBRILS Each myofibril is made of many protein filaments called MYOFILAMENTS. There are two types: MYOSIN – thick filaments ACTIN – thin filaments Actin and Myosin filaments are arranged in an overlapping pattern of light (“I” bands) and dark (“A” bands). In the middle of each “I” band is a line called a “Z” line. The section of a myofibril from one Z-line to the next Z-line is called a SARCOMERE. The arrangement of these sarcomeres next to each other produces the STRIATIONS of the skeletal muscle fibers. Each Myofibirl is surrounded by a network of membranous channels called SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM. Other “tubes” between the actin and myosin filaments the filaments slide between each other this shortens the myofibrils which in turn shorten the muscle fibers, which shortens the muscles “Calcium Pump” returns CA++ into the S.R. (requires energy- ATP) Enzyme Cholinesterase stops action of Acetylcholine II. ENERGY SOURCE: Provided by ATP around myofibrils. ATP is produced by cellular respiration which occurs in the mitochondria (requires O2 and glucose) * Creatine Phosphate provides energy for the regeneration of ATP * Only 25% of energy produced during cellular respiration is used in metabolic processes – the rest is in the form of HEAT. This is what produces our body heat and maintains body temperature. More muscle activity = more heat ATP= adenosine triphosphate ADP = adenosine diphosphate Label Practice Fascicle Endomysium (2) Bone Muscle Fiber Epimysium Perimysium Tendon