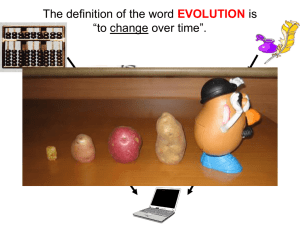
Theories and Patterns of Evolution
advertisement

THEORIES AND PATTERNS OF EVOLUTION Chapter 15 Theories of Evolution Biological Evolution: the change of populations of organisms over time New life forms are really modified versions of older ones in same geographic area 2 Explanations: Lamarck’s Darwin’s Jean Baptiste Lamarck Thought acquired traits (learned, not inherited) could be passed to offspring Not True!! Charles Darwin Spent 5 years aboard H.M.S. Beagle traveling world & recording observations Animal adaptations and geographic changes required VERY LONG periods of time to occur Modern Evolutionary Thought Natural Selection: organisms best suited to their environments will reproduce more successfully Over time, # organisms with favorable traits increases within a population Artificial Selection: Breeding organisms with specific traits to produce desired offspring Modification by Natural Selection The Process: 1) Organisms better equipped to survive environment will produce more offspring 2) Eventually, popltn made up of only successful members 3) Over time, an entirely new species may form!! Descent with Modification “Newer forms appearing in fossil record are actually modified descendants of older species” Implies that ALL species descended from only a few ancient organisms Adaptation Populations adapt as their # of favorable traits increases The types of traits that are favorable depends on the environment Examples: Mimicry: a harmless species resembles a dangerous one; both are avoided by predators Penicillin-resistant bacteria, rose thorns, etc. Camouflage: enables species to blend with surroundings As genetic makeup of popltn changes, evolution occurs Patterns of Evolution The pattern & speed with which organisms adapt is dependent upon their environment 3 Patterns: 1) Coevolution 2) Convergent Evolution 3) Divergent Evolution Coevolution Coevolution: the change of 2 or more species in close association i.e. predator/prey; parasite/host; plants/herbivores Convergent Evolution Convergent Evolution: occurs when environment selects phenotype Results in similar phenotypes of different organisms i.e.: body shape of dolphin (mammal) & shark (fish) Divergent Evolution Divergent Evolution: when 2 related species become more dissimilar Adaptive Radiation: when different species evolve from common ancestor i.e.: Galapagos finches