Patient-Centered Care - Jignasa Pancholy, RN
advertisement

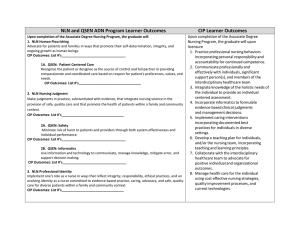
Group 1 Mariel Lontoc Josephine Macaraig Jignasa Pancholy Recognize the patient or designee as the source of control and full partner in providing and coordinated care based on respect for patient’s preference’s, values and needs. (QSEN). Information and skills acquired through experience or education The theoretical and practical understanding of a subject. Definition Creative thinking vs reflective thinking Application in professional Nursing practice. Gather all pertinent information Collaborate with the team Use critical thinking and problem solving skills Consider patients values, beliefs and goals when appropriate. Assessment Diagnosis PLAN Evaluate Implement 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 Central Concepts: Human beings Environment Health Nursing Continuity of Care Assuring coordination Integration Communication Ms. N 70 y.o. female c/o left labial pain, hematuria x3d Hx: DM, HTN, CKD, CAD, PVD, DN Arrived from Philippines. ‘97 Separated from husband 6 children $300 income SSI Guest friends house Temp 98.2 BP 155/42 HR 55 RR 22 No mention of pain A & Ox3 Ambulatory Day 1 HD, treated for UTI Day 3 Gyn Consult noted fluctuance on labial lesion 4x3cm Transferred to ACE unit Assess patient cognition- MINI COG Monitor ADL, baseline function Ambulation Communal dining Activities IPOC rounds HD 3x week While waiting for a HD slot-pt transferred to a regular floor Two weeks-developed progressive difficulty ambulating Gait unsteady, assist with ADL’s D/C to SNF Law and Ethics Ethical standard: Consider the patient’s wishes and goals Care for the whole patient Legal standard: What would a reasonably prudent nurse in like or similar circumstances do? Respecting, Recognizing and Understanding patients cultural and social values along with ethical responsibilities in patients outcome. Culture Transcultural nursing Multicultural nursing Examination of personal Values, Beliefs , Biases, and prejudices. Cultural Awareness Specific Communication Strategies Interaction with Different Cultures Mistake Identification and Acknowledgement Remediation for Cultural Mistakes Culturally Congruent Care Multi Cultural Professionalism must occur. Understanding physical appearance variations Understanding variation in philosophy Ms. N was one of the victim of Hospital – Associated Disability Ms. N was an immigrant from Philippines and her primary language was Tagalog Ms. N came for pain on her libia Ms. N was placed in long term care Preventing Hospital Acquired Disability Team collaboration Continuity of care Client Advocate and Attitude Knowledge Skills Attitude Betancourt, J. R. (2004, September 2). Cultural Competence — Marginal or Mainstream Movement? The New England Journal of Medicine, 351(2004), 953-955. Covinsky, K. E., Pierluissi, E., & Johnston, B. C. (2011, October 26). Hospitalization-Associated Disability. JAMA, 306(16), 1782-1793. Retrieved from jama.ama-assn.org QSEN - Quality & Safety Education for Nurses. (n.d.). Retrieved February 19, 2012, from http://www.qsen.org/ Jama.ama-assn.org@ucsf.edu http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SSauhroFTpk Assessment tools (see forms) Hood 7th edition 2009 www. QSEN.ORG Jama.ama-assn.org@ucsf.edu http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SSauhroF Tpk Assessment tools (see forms) Hood 7th edition 2009