The Islamic Empires
advertisement

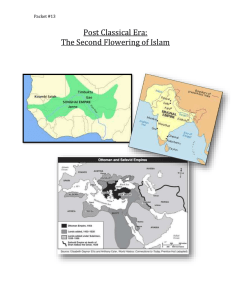
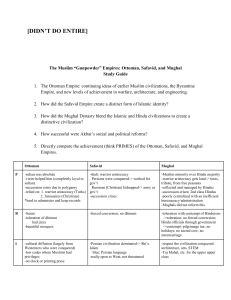
1450 - 1800 Concepts & Terms Ethnocentrism Safi al-Din Sulemaniye Mosque Imams Janissaries Vizier Chalderan Mullahs Isfahan Shah Sikhs Padishah Marattas People Mehmed II Abbas I [Great] Babur Humayan Akbar Din-i-Ilahi Nadir Khan Afsher Mumtaz Mahal Aurangzeb Nur Jahan Isma’il Safi al-Din Ottoman Safavid Essential Questions How did the Shi’a / Sunni split effect relations in Dar al-Islam 1450 to 1800? What is the political difference b/w the Ottomans and the Safavids? How does cultural conservatism impact the future of the Ottoman Empire? Why is there little impact from the biological exchanges of exploration in Dar al-Islam? Ottoman Empire Osman Bey Founder Central Asian steppes- original location [Turks] Powerful military Ghazi - light cavalry Janissaries – slave troops DEVSHIRME – Balkan contributions Young Christian boys – slave tribute Captured Constantinople 1453 – Istanbul Expanded into Serbia, Greece, Albania Constantinople / Istanbul Ottoman Expansion Suleiman the Magnificent 1556] Into Syria– Egypt -Southwest Asia Middle East Into Europe To Vienna, Italy, Malta Powerful navy Challenged European fleets Lepanto – defeated by Spain 1571 [1495- Ottoman – Safavid Rivalry Ottomans Ruled from Turkey Sunni Persecuted Shia Secular Government Victory at Chalderan Safavid: [Shah] Shia Successors of Persia Less secular Ruled from Iran Defeated Uzbeks Central Asia Safavid Empire / Shah Abbas Mughal Dynasty Babur Descendent of Timur I lang Akbar Centralized government Expanded into southern Aurangzeb Entire Indian subcontinent Provoked the hostility of Hindus Taxation & destroyed Hindu temples India Ottoman Imperial Rule Dynastic state [not Islamic state] Military creation Prestige & authority derived from piety Sultans: [Turk Ruler] Ruled w/o regard to religious or social traditions Contested succession Agriculture Food and cash crops Wheat & rice Tobacco Coffee houses b/c popular American crops did not impact Result > low population greatly growth Trade Ottoman & Safavid Occupied trade routes Active involvement in global trade Precludes the need to participate in New World trade. Mughal Not as focused on trade Empire was enriched by trade Because of location Wealth Through Trade Religion & Empire Diversity often challenged rule Christian missions Goa - center of Portuguese missions Jesuits - failed to convert Akbar who embraced the synchronized religion of Sikhs Religious minorities Conquered people protected Cooperation b/w Muslims & Hindus Mughal GOA Famous Buildings Taj Mahal <> Islamic Capitals ISTANBUL Constantinople Ottoman Empire Fatehpur Sikri abandoned b/c poor water supply Topkapi Palace Sultan’s residence Suleymaniye blend of Byzantine and Islamic elements Mughal Empire Taj Mahal famous tomb and mosque Empires in Transition Deterioration of Leadership 16th & 18th Centuries negligent rulers - factions - corruption Religious tensions b/c conservatives Abandoned religious tolerance Ottomans- protested telescope & printing press Safavids-persecuted Sunnis, Sufis, non-Muslims Mughals- Aurangzeb’s anti-Hindu policies Decline ECONOMIC DECLINE Reversal of expansion caused: Official taxation Corruption Lost initiatives to European merchants MILITARY DECLINE Imported European weapons No internal armament industries Unable to maintain technological edge in armaments Cultural Insularity Cultural Conservatism Confident of cultural superiority Ignored European cultural & technological developments Ottomans: Banned printing in Arabic & Turkish Mughals: no interest in printing technology Islamic rulers preferred stability avoided the risks of imported cultural & technological innovations Enduring Question Give examples of cultural conservatism [cultural insularity] at work in the world today.