In terms of biology, the female sex organs
are involved in the reproductive system,
whereas
the
secondary
sex
characteristics are involved in nurturing
children or, in some cultures, attracting a
mate.
Asserts the equality of men and women
through political and legal reform.
It is an individualistic form of feminism,
Focuses on women’s ability to show and
maintain their equality through actions and
choices.
Uses the personal interactions between men
and women as the place from which to
transform society.
Women can free themselves only when they
have done away with what they consider an
inherently oppressive and dominating system.
Feel that there is a male-based authority and
power structure and that it is responsible for
oppression and inequality.
Some see no alternatives other than the total
uprooting and reconstruction of society in
order to achieve their goals.
Argues that sexism, class oppression, and
racism are inextricably bound together.
Forms of feminism that strive to
overcome sexism and class oppression
but ignore race can discriminate against
many people, including women, through
racial bias.
Divided by classes / castes
Only the elites are given proper training
but not education
Are seen as merely tools
Respect is earned if they sided with the
friars or marry a “peninsulares” or
“insulares”
Liberalized Filipino
women
Education was
received
Exploitation
Abused Women
Comfort Women
Still dominated and unequally treated
Allowed employment but not
managerial jobs
“Glass ceiling”
Crimes
Women’s rights are recognized
Priority is given
Fighter
Represented
Discrimination is lesser
Projected Population in the
year 2008
INDICATOR
Population
Projected
Population
Projected Life
Expectancy at
Birth
WOMEN
MEN
45,483,100
44,974,100
71.6 years
66.1 years
Description
Male
Percentage
Female
Percentage
Single
13,278,500
52.9
11,800,711
47.1
Legally
Married
13,016,984
49.9
13,071,239
50.1
Widowed
571,789
24.3
1,781,382
75.7
Separated
202,007
36.2
356,016
63.8
1,541,041
50.3
1,520,125
49.7
Live-in /
Others
Highest Educational Attainment
Criteria
WOMEN
MEN
Functional Literacy Rate
86.3
81.9
Simple Literacy Rate (%)
92.3
92.0
No Grade Completed
5.9
6.0
Pre-School
2.3
2.3
Elementary
40.7
43.1
Secondary
28.8
28.0
Post Secondary
3.7
4.0
College Undergraduate
10.3
9.8
College Graduate and Higher
5.5
3.9
Criteria
Women
Men
Most Common Field
of Study
Business
Administration and
Related Programs
Engineering
Technology and
Related Programs
Most Common
Program in
Technical
Vocational
Education
Trade, Craft, and
Industrial Programs
Trade, Craft, and
Industrial Programs
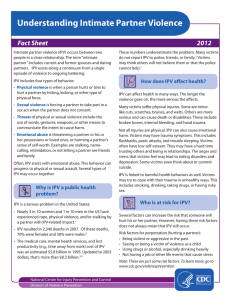
Violent acts that are primarily or exclusively
committed against women.
Targets a specific group with the victim's
gender as a primary motive.
Women are more likely to be victimized by
someone that they are intimate with,
"Intimate Partner Violence" or (IPV).
The impact of domestic violence can be
understood through the example that 40-70%
of murders of women are committed by their
husband or boyfriend.
Domestic violence
› "Intimate Partner Violence" or (IPV)
› not always perpetrated as a form of physical
violence but can also be psychological and
verbal
State violence
› Sex slavery
› Violence in empowerment systems
Gender inequality refers to the obvious or
hidden disparities among individuals based
on performance of gender
› Income disparities in job stratification
› Stereotyping
› Gender roles at home
Prostitution is sexual activity in exchange for
money.
The legal status of prostitution varies greatly
between different countries, from being
punishable by death to being completely
legal.
› Prostitution or being a prostitute is a legal
profession in Thailand.
Abortion is the removal or expulsion of an
embryo or fetus from the uterus, resulting in or
caused by its death.
› In the Philippines, abortion is not legal due to our
faith.
› In other countries (USA) this is as legal as any other
medical procedure.
Rape
Sexual Harassment
Acts of Lasciviousness
Incest
Convention on the Elimination of All
Forms of Discrimination Against Women
(CEDAW)
New Family Code of 1987 affirms
women's right to own property and to
contract employment and credit without
the need of their husbands' consent.
Comprehensive Agrarian Reform Law of
1988 guarantees equal rights to land
ownership, equal shares of the farm's
produce, and representation in advisory
or appropriate decision-making bodies
to qualified women of the agricultural
work force
Legislation of 1990 mandates the
establishment of day care centers in
every village to free women for other
activities such as farming or attending
extension and other meetings.
The Women in Development and Nation
Building Act of 1992 provides equal
access to resources, including credit and
training. It also requires the allocation of
a substantial portion of Official
Development Assistance (ODA) funds to
support programmes and activities for
women.
Commonwealth Act No. 647 an Act to
grant maternity leaves to married
women.
General Assembly Binding Women for Reforms, Integrity,
Equality, Leadership, and Action
ーIn honor of Gabriella Silang
Seek to transform women into an organized political
force.
a movement dealing distinctly with the problems of
women as women, working to free women from all
forms of economic and political oppression and
discrimination, sexual violence and abuse, neglect
and denial of their health and reproductive rights
a movement integral to the national liberation
struggle for sovereignty, a democratic and
representative government and equality between
women and men in all aspects of life
a vital movement to harness the power of half of the
country's population towards liberation
ーNamed after the Egyptian Goddess Isis
is a feminist NGO committed to creating
spaces within information and
communications structures and systems that
promote the many voices of women,
particularly those from the South.
Phenomena of globalisation, gender,
ethnicity and religion that intersect and
impact on women’s lives.
Department of Social Welfare and Development
Participates in addressing issues of (UNCEDAW) United Nations – Convention
on the Elimination of All Forms of
Discrimination Against Women。
National Family Violence Prevention
Program which teaches family members
to protect themselves against violence
and manage peaceful resolution of
conflict within the family.
review, evaluate, and recommend
measures, including priorities to ensure
the full integration of women for
economic, social and cultural
development at national, regional and
international levels, and to ensure further
equality between women and men.”
Organizing women into a nationwide
movement called "Balikatan sa Kaunlaran"
(shoulder-to-shoulder in development).
Conducting policy studies and lobbying
for the issuance of executive and
legislative measures concerning women
Establishing a clearinghouse and
information center on women
Monitoring the implementation of the
UNーCEDAW