Earth Sys Study Guide Ch 5, 6, 7
advertisement
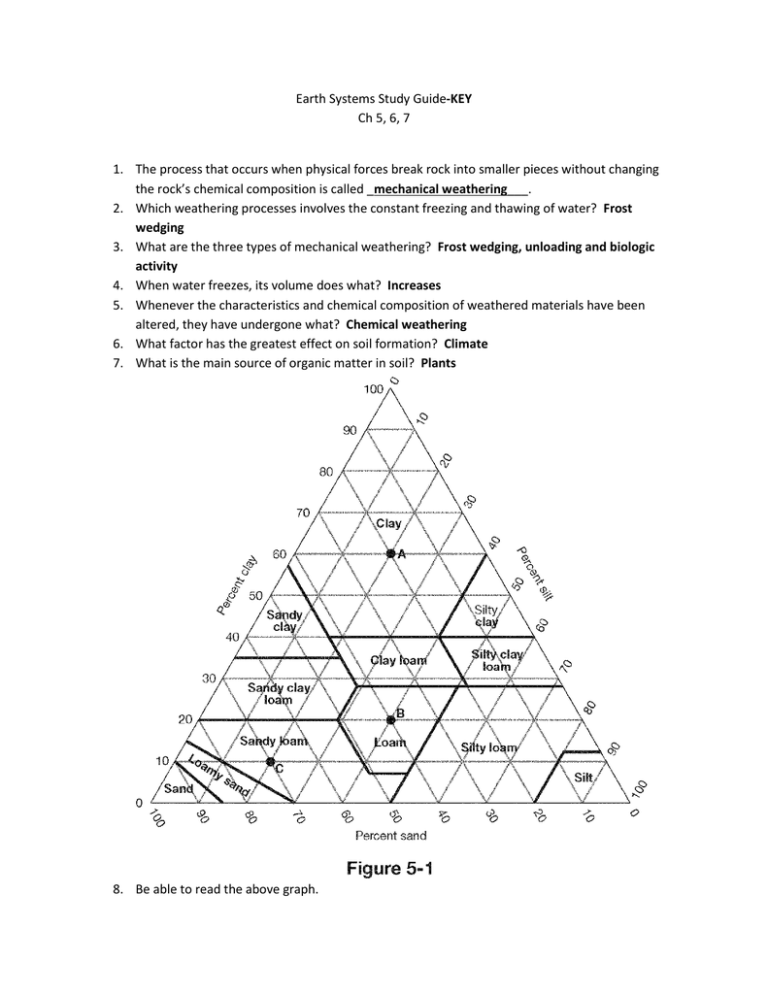
Earth Systems Study Guide-KEY Ch 5, 6, 7 1. The process that occurs when physical forces break rock into smaller pieces without changing the rock’s chemical composition is called _mechanical weathering___. 2. Which weathering processes involves the constant freezing and thawing of water? Frost wedging 3. What are the three types of mechanical weathering? Frost wedging, unloading and biologic activity 4. When water freezes, its volume does what? Increases 5. Whenever the characteristics and chemical composition of weathered materials have been altered, they have undergone what? Chemical weathering 6. What factor has the greatest effect on soil formation? Climate 7. What is the main source of organic matter in soil? Plants 8. Be able to read the above graph. 9. In a well-developed soil profile, which horizon is the uppermost layer? The A horizon 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Label the above figure. X=a horizon, Z=b horizon, W=C horizon, Y=Parent material How are soil horizons ordered from the top of the profile to the bottom? A, B, C The B horizon is also called the _Subsoil___. A soil that is characteristic of the humid eastern United States is _Pedalfer___. Since humans have appeared, the amount of sediments carried by rivers has _Increased alot___. (increased a lot, increased a little, or stayed the same?) 15. The process responsible for moving material downslope under the influence of gravity is called __Mass movement__. 16. What factor commonly triggers mass movements? 1) earthquakes and 2) saturation of surface materials with water 17. Why do over steepened slopes often lead to mass movements? The angle of their slope is greater than 40 degrees 18. What is the slowest type of mass movement? Creep 19. A relatively rapid form of mass movement that is most common in dry mountainous regions is _a mudflow___. 20. Define slump. Slippage of a block of material moving along a curved surface 21. Alternate freezing and thawing often leads to what? Creep 22. Plants release water into the atmosphere through a process called what? Transpiration 23. What influences stream velocity? Channel size and shape and stream gradient 24. Where does a stream’s discharge increase? Between its source and mouth 25. In a typical stream, where the gradient is steep, is the discharge large or small? Small 26. Where do most streams carry the largest part of their load? In suspension 27. What is the measure of the largest particles a stream can carry? Competence 28. In a stream channel, what will be deposited first? Gravel-size particles 29. What is a drainage basin? The land area that contributes water to a stream. 30. What are the boundaries called that separate streams in adjacent drainage basins? Divides 31. Label the above diagram. A=Spring, B=Aquitard, C=Main water table, D=Zone of Saturation, E=Zone of aeriation, F=Unsuccessful well, G=Successful well 32. When groundwater enters underground fractures or caverns in hot igneous rocks, where it is heated to boiling temperatures, what feature can form? Geyser 33. Which direction do ice sheets flow? In all directions 34. 35. 36. 37. Which ice sheet holds almost two-thirds of Earth’s fresh water? Antarctic Ice Sheet The loosening and lifting of blocks of rock by glaciers is called what? Plucking Material deposited directly by a glacier is called what? Till Icebergs are produced when large pieces of ice break off from the front of a glacier during a process called _Calving___. 38. Glacial movement depends on the balance between _Accumulation___ and ___Wastage________. 39. Label the above figure. A=Drumlin field, B=End Moraine, C=Esker, D=Till, E=Ground Moraine, F=Kettle lake,G=Outwash plain 40. During the most recent ice age, what percentage of Earth’s surface was covered by glaciers? 30% 41. Why can a heavy rain shower cause a large amount of erosion in a desert area? There is a lack of vegetation to hold the soil in place. 42. Define abrasion. Windblown sand cutting and polishing exposed rock surfaces 43. What is a blowout? A shallow depression caused by deflation 44. Deflation affected the Dust Bowl in the 1930s by doing what? Lowering the land 45. In desert areas, what process results in the formation of a desert pavement? Deflation 46. Sand dunes that form scalloped rows of sand at right angles to the wind are called __Barachanoid __ dunes. 47. Label the above types of sand dunes. A=Barchan dunes, B=Transverse Dunes, C=Barchanoid Dunes, D=Longitudinal Dunes 48. Define creep. The slowest type of mass movement, involves the lifting and contracting of soil particles over time. 49. Define chemical weathering. The process that changes rock into one or more new compounds. 50. Define abrasion. The process in which rock surfaces are cut and polished by windblown sand. 51. Define mechanical weathering. Weathering that involves physical forces that break rock into smaller pieces. 52. Define regolith. The upper portion of the soil that supports plant growth.