Analyze - Hypothesis Testing Normal Data
advertisement

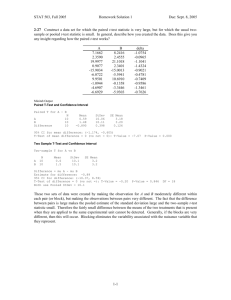
Paired t-test Exercise Exercise objective: Utilize what you have learned to conduct and analyze a paired t-test using MINITABTM. 1. A corrugated packaging company produces material which has creases to make boxes easier to fold. It is a critical to quality characteristic to have a predictable Relative Crease Strength. The quality manager is having her lab test some samples labeled 1-11. Then those same samples are being sent to her colleague at another facility who will report their measurements on those same 1-11 samples. 2. The US quality manager wants to know with 95% confidence what the average difference is between the lab located in Texas and the lab located in Mexico when measuring Relative Crease Strength. 3. Use the data in columns “Texas” & “Mexico” in “RM Suppliers.mtw” to determine the answer to the quality manager’s question. OSSS LSS Green Belt v10.0 - Analyze Phase 1 © Open Source Six Sigma, LLC Paired t-test Exercise: Solution Because the two labs ensured to exactly report measurement results for the same parts and the results were put in the correct corresponding row, we are able to do a paired ttest. The first thing we must do is create a new column with the difference between the two test results. Calc>Calculator OSSS LSS Green Belt v10.0 - Analyze Phase 2 © Open Source Six Sigma, LLC Paired t-test Exercise: Solution We must confirm the differences (now in a new calculated column) are from a Normal Distribution. This was confirmed with the AndersonDarling Normality Test by doing a graphical summary under Basic Statistics. Summary for TX_MX-Diff A nderson-Darling N ormality Test -0.50 -0.25 0.00 0.25 0.50 A -S quared P -V alue 0.45 0.222 M ean S tDev V ariance S kew ness Kurtosis N 0.22727 0.37971 0.14418 -0.833133 -0.233638 11 M inimum 1st Q uartile M edian 3rd Q uartile M aximum 0.75 -0.50000 -0.10000 0.40000 0.50000 0.70000 95% C onfidence Interv al for M ean -0.02782 0.48237 95% C onfidence Interv al for M edian -0.11644 0.50822 95% C onfidence Interv al for S tD ev 95% Confidence Intervals 0.26531 0.66637 Mean Median 0.0 OSSS LSS Green Belt v10.0 - Analyze Phase 0.2 0.4 3 0.6 © Open Source Six Sigma, LLC Paired t-test Exercise: Solution As we’ve seen before, this 1 Sample T analysis is found with: Stat>Basic Stat>1-sample T OSSS LSS Green Belt v10.0 - Analyze Phase 4 © Open Source Six Sigma, LLC Paired t-test Exercise: Solution Even though the Mean difference is 0.23, we have a 95% confidence interval that includes zero so we know the 1-sample t-test’s null hypothesis was “failed to be rejected”. We cannot conclude the two labs have a difference in lab results. Histogram of TX_MX-Diff (with Ho and 95% t-confidence interval for the mean) 5 The P-value is greater than 0.05 so we do not have the 95% confidence we wanted to confirm a difference in the lab Means. This confidence interval could be reduced with more samples taken next time and analyzed by both labs. OSSS LSS Green Belt v10.0 - Analyze Phase Frequency 4 3 2 1 0 _ X Ho -0.50 5 -0.25 0.25 0.00 TX_MX-Diff 0.50 0.75 © Open Source Six Sigma, LLC