Food Chains - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

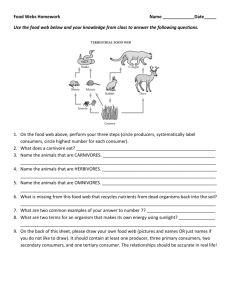
Food Chains • Food Chain • A series of events in which one organism eats another and obtains energy. • What do food • Food chains show the transfer of chains show? energy in an ecosystem • What do the • The arrows represent the transfer arrows of energy. represent? • What do food chains start with? • What type of organism is after the sun? • Describe photosynthesis. • All Food Chains start with the sun • After the sun is an organism that can do photosynthesis. Like plants and phytoplankton. • Sunlight + Carbon Dioxide + Water = Energy This process is called Photosynthesis • Sample food • Sun →milkweed → aphid →ladybug chains: →bird → mushroom • Sun → grass → zebra → lion → vulture • Sun → seeds → grasshopper→ mouse → hawk Video Clip • Producers Flowers Phytoplankton • An organism that can make its own food . They use carbon dioxide, water and sunlight to make energy, through a process called photosynthesis. Producers are the source of all food in an ecosystem. Without producers there is no food chain. Tree • Decomposers • Organisms that break down wastes and dead organisms and return the raw materials to the environment. • Two major groups of decomposers are: – Bacteria – Fungi. Decomposer Video Clip • Consumers • An organism that obtains energy by feeding on other organisms. • Ex: Deer, Humans, Snakes, Bat, Cat, Hippopotamus, Cricket, Rabbit • 3 types of Consumers • Herbivores, Omnivores and Carnivores • Food Chain Game • Sample food • Sun →milkweed → aphid →ladybug chains with producer 1 consumer 2 consumer energy roles →bird → mushroom labeled: 3 consumer Decomposer • Sun → grass → zebra → lion → vulture produce 1 consumer 2 consumer 3 con • Sun → seeds → grasshopper→ mouse → producer 1 consumer hawk 3 consumer Video Clip 2 /Prod/Cons Video 2 consumer • 3 types of consumers • Carnivores • Herbivores, Carnivores, and Omnivores • Consumers that eat ONLY other consumers. ( Meat -Eaters) • Ex: T-rex, Tigers, Lions, Ladybugs, Spiders. • Herbivores • Herbivores are consumers that eat only producers. (plant eaters) • Ex: Butterflies, deer, elephants, giraffes, mice. • Omnivores • Consumers that eat BOTH consumers and producers. (both meat eaters and plant eaters) • Ex. Humans, Bearded Dragons, Turtles, Bears. • Sample • Sun →milkweed → aphid →ladybug food producer 1 consumer 2 consumer chains herbivore Carnivore with →bird → mushroom energy 3 consumer Decomposer roles Omnivore labeled: • Sun → grass → zebra → lion → vulture produce 1 consumer 2 con 3 con herbivore carnivore carnivore • Food Webs • A Food Webs consists of many overlapping food chains in an ecosystem. • It better represents the transfer of energy than a food chain. • Energy Pyramid • An Energy Pyramid shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web. The most energy is at the producer level. At each level there is less available energy. • Energy Pyramid Video Clip