Directing - WordPress.com
advertisement

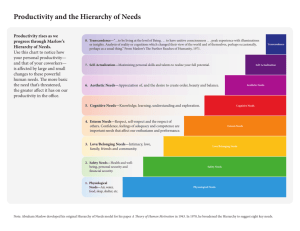
Directing Meaning Management is an art of getting the done through others. The term, Direction, stands for that managerial function which initiates organized action. Directing means telling people what to do and seeing that they do it as per plan. Definition According to Earnest Dale defines directing as ,. telling people what to do and seeing that they do it to the best of their ability. It includes making assignment , explaining procedures, seeing that mistakes are corrected , providing on the job instruction, and of course, issuing order. Nature & Characteristics • It is a dynamic function: A manger has to continuously direct, motivate , guide and lead his subordinates. • It initiate action • It provide necessary link between various managerial functions • It is universal function • It is concerned with human relationships Principle of effective direction • Harmony of objective • Unity of Command • Unity of direction • Direct supervision • Effective communication • Follow ups Motivation Meaning At one time, employees were considered just another input into the production of goods and services. Motivation is the driving force by which humans achieve their goals It is the incentives that we seek, the perks that bubble. It is a gentle yet invisible hand that pushes us forward. Definition “A motive is an inner state that energizes, activates or moves and direct or channels behavior goals” -Berleson and Stenier “It is the stimulation of any emotion or desire operating upon one’s will and promoting or driving it to action” Importance of motivation in Management Motivating the staff is a very critical factor for the following reasons: • Resulting in higher output or productivity meaning that given a certain level of resources, a highly motivated workforce will generate very much more than a de-motivated workforce • Reduces wastages and produce more higher quality works • Motivated staff are generally more pro-active and has greater sense of urgency hence making things happen faster • Motivated staff will give their best to the company hence helping management to achieve the organization objectives like achieving sales and profit targets. Types of Motivation There are two ways in which people can be motivated: • Positive Motivation or Pull Mechanism: When shown a reward and a way to achieve it. Such a reward may be financial or non-financial. Monetary motivation may include different incentives, wage plans, productive bonus schemes, etc.. • Non-Monetary motivation may include praise for work, participation in management , social recognition etc.. Generally seeks to create a positive atmosphere in the organisation. Types of Motivation • Negative Motivation or Push Mechanism: Installing fear in the minds of the people.. Fear of consequences of doing something or not doing something keeps the worker in desired direction. Fear creates frustration and an unfavorable attitude towards work which hinders efficiency and productivity. Its use should be kept minimum. Theories Of Motivation A large number of theories exist on motivation but among them there are few theories that are considered to be outstanding. These Theories explain the various approaches to motivation. The following theories will be discussed: • Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs • Herzberg’s Motivation Hygiene Theory & • McGregor’s X and Y Theory Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs One of the most widely mentioned theories of motivation is the hierarchy of needs theory put forth by psychologist Abraham Maslow. • Physiological needs: These are important needs for sustaining the human life. Food, water, warmth, shelter, sleep, medicine and education are the basic physiological needs which fall in the primary list of need satisfaction. • Security or Safety needs: These are the needs to be free of physical danger and of the fear of losing a job, property, food or shelter. It also includes protection against any emotional harm. • Social needs: Since people are social beings, they need to belong and be accepted by others. People try to satisfy their need for affection, acceptance and friendship. Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs • Esteem needs: Once people begin to satisfy their need to belong, they tend to want to be held in esteem both by themselves and by others. This kind of need produces such satisfaction as power, prestige status and self-confidence. It includes both internal esteem factors like self-respect, autonomy and achievements and external esteem factors such as states, recognition and attention. • Need for self-actualization: It is the drive to become what one is capable of becoming, it includes growth, achieving ones potential and self fulfillment. It is to maximize one’s potential and to accomplish something. Douglas McGregor’s Theory X and Y McGregor, in his book .The Human side of Enterprise. States that people inside the organization can be managed in two ways. The first is basically negative, which falls under the category X and the other is basically positive, which falls under the category Y. Under the assumptions of Theory X • Employees inherently do not like work and whenever possible, will attempt to avoid it. • Because employees dislike work, they have to be forced, coerced or threatened with punishment to achieve goals. • Employees avoid responsibilities and do not work fill formal directions are issued. • Most workers place a greater importance on security over all other factors and display little ambition. Douglas McGregor’s Theory X and Y In contrast under the assumptions of Theory Y: • Physical and mental effort at work is as natural as rest or play. • People do exercise self-control and self-direction and if they are committed to those goals. • Average human beings are willing to take responsibility and exercise imagination, ingenuity and creativity in solving the problems of the organization. On analysis of the assumptions it can be detected that theory X assumes that lower-order needs dominate individuals and theory Y assumes that higher-order needs dominate individuals. In contrast Theory Y organizations can be described as participative., where the aims of the organization and of the individuals in it are integrated; individuals can achieve their own goals best by directing their efforts towards the success of the organization. Frederick Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene theory Frederick Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene theory Frederick has tried to modify Maslow’s need Hierarchy theory. His theory is also known as two-factor theory or Hygiene theory. He stated that there are certain satisfiers and dis-satisfiers for employees at work. • Intrinsic factors are related to job satisfaction, while • Extrinsic factors are associated with dissatisfaction. He asked people to describe in detail, such situations when they felt exceptionally good or exceptionally bad. • From the responses that he received, he concluded that opposite of satisfaction is not dissatisfaction. •Removing dissatisfying characteristics from a job does not necessarily make the job satisfying. •He states that presence of certain factors in the organization is natural and the presence of the same does not lead to motivation. Frederick Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene theory However, their non presence leads to de-motivation. In similar manner there are certain factors, the absence of which causes no dissatisfaction, but their presence has motivational impact. Morale Meaning Morale is purely emotional. Its an attitude of an employee towards a job, his superior and his organisation. This may vary from high to very low. It changes depending on work conditions, superiors, fellowworkers, pay and so on. When an employee has a favourable attitude towards his work, he is said to have high morale. Definition: “Morale is a state of mind or of a willingness to work which in turn affects individuals and organisational objectives.” -Michael J. Jucius Leadership Definition Leadership is the ability of a manager to induce subordination to work with confidence and Zeal. - Koontz and O. Donnel Leadership is activity of influencing people to strive willingly for group objectives. -George R.Terry Leadership Styles • Authoritarian or autocratic • Participative or democratic • Delegative or Free Reign(Laissez faire) • Paternalistic Communication Communication is the best means by which people are linked together in an organisation to achieve a common objective or purpose. It is the life blood of organisation. Meaning The word communication has been derived from the Latin word “communis” which means common. Thus communication means sharing of ideas in common. Communication Definition “Communication is a way that one organisation member shares meaning and understandings with another” - Koontz & O'Donnell Principle of effective communication system •Clarity and completeness of message • Adequate Briefing of the recipient • Integrity and Sincerity • Motivation and mutual confidence • Proper feedback • Proper Timing • Use of appropriate media • Use of informal organisation • Emphatic listening and avoiding premature evaluation • Sound organisation structure Co-ordination Co-ordination is the process of synchronizing activities of various persons in the organization in order to achieve goals. Definition: To co-ordinate is to harmonies all the activities of a person in order to facilitate its working and its success. -Henry Fayol It seems more accurate to regard co-ordination as the essence of manger ship for achievement of harmony of individual efforts towards the accomplishment of group goal is the purpose of management. Each of the managerial functions is an exercise in co-ordination. -Koontz and O'Donnell Importance of co-ordination Co-ordination is essential at every level of management for achieving harmony of individual efforts. • Good personnel relation • Unity of Direction • Essence of management • Efficiency and economy • Helpful in developing and retaining of personnel