Chapter 7 China Dynasties
advertisement

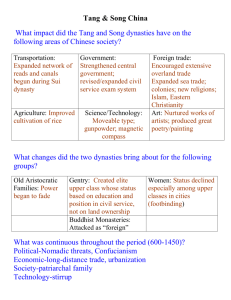
The Chinese Empire Review Chapter 7 The crane is the most popular bird in Chinese history and is a symbol of longevity Period of Disunion 220-589 Period of Disunion p. 166 War was common Nomadic people settled in Northern China. CULTURAL BLENDING Some Chinese adopted nomads’ culture Some nomads adopted Chinese culture Disunion Religion Buddhism spread Quic k Time™ and a decompres sor are needed to s ee t hi s pic ture. Why? It promised an escape from suffering Disunion Government Control of government changed hands often Rival kingdoms were ruled by military leaders. Disunion Economy Not great due to war. Disunion Culture/Arts & Inventions Blending of cultures created new types of art and music. New foods and clothing styles also developed SUI DYNASTY p. 167 589-618 Short period (29 years). Grand Canal Quic kTime™ and a dec ompres sor are needed to see this pic ture. Sui Dynasty Yang Jian took over China and 1. 2. 3. 4. ended the years of Disunion. He conquered the south unified China created SUI Dynasty and restored order in China. Sui Religion Buddhism very popular and also: Confucianism Daoism QuickTi me™ and a decompressor are needed to see thi s pi ctur e. Sui Economy Grand Canal was built that linked northern and southern China. Sui Culture/Arts & Inventions Grand Canal major accomplishment during the Sui. Tang Dynasty 618-907 (289 years!) Tang Geography (map p. 167) China grew under Tang Dynasty It included eastern Asia and central Asia. Tang (continued) It is called “The Golden Age of China” Why? Three Important Tang Rulers 1.Taizong p. 167 Helped unified China through 1. Programs 2. Reformed military 3. Created new laws codes 4. Created land reform policy called equal field system, Tang Rulers (con’t) 2. Xuan-zong P. 167 was another great ruler. During his reign 1. culture flourished 2. many fine poets wrote during his reign. Tang Rulers (con’t) 3. Empress Wu p.167 - was another Tang ruler in 655. 1. Only woman to rule China. 2. She was vicious but intelligent and talented. 3. She brought stability and prosperity to China. Tang Religion BUDDHISM Buddhism grew until a Tang emperor launched a campaign against the religion. He burned many Buddhist texts and destroyed many temples, but he did not destroy Buddhism completely. Tang Religion continued Buddhism changed when it blended with two other philosophies: 1. Confucianism-to improve Chinese government and society. 2. Daoism Tang Economy Economy was GREAT! Advances in agriculture. FOOD surpluses helped trade and population. Cities grew. China became very rich! Tang Culture/Arts & Inventions Qui ckTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see thi s pi cture. Porcelain -first made during Tang Dynasty. Woodblock printing was invented during Tang. Printers could copy drawings or texts quickly. Gunpowder was invented during late Tang for fireworks. Magnetic compass was improved by the Tang. Tang Culture/Art (con’t) The artists and writers of the Tang Dynasty were some of the greatest in China. Wu Daozi painted murals. Li Bo and Du Fu wrote poems. Tang artists made clay figures of horses. Tang Culture-Foot Binding In the Tang dynasty they practiced foot binding. Foot binding was first practiced among the elite and only in the wealthiest parts of China. Foot binding showed others that these well-born girls were free from manual labor and had husbands who could afford wives who did not need to work. This practice was banned in China in 1912. Foot Binding QuickTi me™ and a decompressor are needed to see thi s pi ctur e. Quic kTime™ and a dec ompres sor are needed to see this pic ture. Quic kTime™ and a dec ompres sor are needed to see this pic ture. Quic kTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this pic ture. QuickTime™ and a decom press or are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Song Dynasty p. 168 960-1279 (319 years!) China again reunified. Song This was a period of great accomplishments! Song Economy Agriculture helped the economy During the Song farming reached new heights. Improvements in irrigation (called the dragon backbone pump) allowed one person to do the work of several. Fast-ripening rice allowed farmers to grow 2-3 crops in the time of one. Song Economy (continued) Crops were introduced: 1. Cotton 2. Tea EXTENSIVE TRADE BROUGHT WEALTH DURING THE SONG! Song Banking Chinese financial institutions were conducting all major banking functions, including accepting deposits, making loans, and exchanging money by the Song Dynasty (960-1279). Paper Money QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Song Economy (con’t) Food surpluses helped the government. Food was abundant. Population increased. Cities grew. During the Song, China was the largest Country in the world. Song Religion NEO-CONFUCIANISM The ideas of Confucius had a dramatic effect on the Song system of government. Ideas: 1. Ethics 2. Proper behavior SONG NEO-CONFUCIANISM 1.Government workers worked in a bureaucracy or group of unelected officials. 2. To join the bureaucracy, you had to pass a civil service test. Students spent years studying for the tests. Those who passed were ScholarOfficials or elite members of society. Song Culture/Inventions MOVABLE TYPE Inventors of the Song created movable type which made printing much faster. Carved letters could be rearranged and reused to print many different messages. PAPER MONEY-The world’s first paper money was invented during th Song to manage their money wealth. Song Culture/Inventions MOVABLE TYPE Inventors of the Song created movable type which made printing much faster. Carved letters could be rearranged and reused to print many different messages. PAPER MONEY-The world’s first paper money was invented during th Song to manage their money wealth. Song Culture/Art The Song period was noted for literature. Li Qingzhao was China’s greatest female poet. The Song artists also made porcelain items. YUAN DYNASTY 1279-1368 (89 YEARS) MONGOL RULE YUAN-Mongol Rule Genghis Khan led bloody expeditions to conquer Asia. Kublai Khan, his grandson, declared himself the emperor of China in 1279. This was the first time China was ruled by foreigners Marco Polo Marco Polo, an Italian merchant, wrote a lot about the Yuan Dynasty and served in Kublai Khan’s court. Yuan Culture Mongols spoke a different language. Mongols wore different clothing. Mongols worshiped different gods. Mongols had different customs. Kublai didn’t force the Chinese to accept Mongol ways, but some Mongols adopted some Chinese ways such as Confucianism. Yuan Economy Mongols disrupted many of the great things from the Tang/Song. Mongols kept control of the Chinese and made them pay taxes. Tax money paid for extending the Grand Canal, new roads, and palaces. Sea trade was good between China, India, and Southeast Asia. Fall of the Yuan The Yuan Dynasty fell when they invaded Japan. Violent storms destroyed the forces and weakened their military. The expensive public works projects also weakened the economy and caused rebellion. Fall of the Yuan (con’t) The final fall came when a former monk, Zhu Yuanzhang, led an army to a final victory over the Mongols. China then got back into the rule of the Chinese. Ming Dynasty 1368-1644 (276 years) QuickTi me™ a nd a de com press or are need ed to se e th is p icture. Ming Dynasty Zhu Yuanzhang (p. 183)led rebellion against the Mongols and won a victory. He became the emperor of the Ming Dynasty The Voyages of Zheng He QuickTi me™ a nd a de com press or are need ed to se e th is p icture. Ming Religion All three, with renewed attention to Confucian classics Ming Government Emperors had strong control Ming Economy At first was stable and prosperous Trade and sea voyages made the economy prosperous. Trade increased until the end of the Dynasty when trade was stopped and isolation began. Ming Culture/Arts & Inventions Great ships some longer than a football field. Grand building projects: 1. Forbidden City in Beijing with 9,000 rooms. 2. Restored the Great Wall of China. Ming Great Wall of China Most of the Great Wall that we see today was built or rebuilt during the Ming Dynasty 1368-1644. Soldiers and guards would send signals from the wall. Many people died building the wall (perhaps up to 8 million). QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Ming (continued) The Ming fixed the Yuan Dynasty’s destruction In 1430 foreign trade was banned and China became isolated from the world. CHAPTER 7 Quic kTime™ and a dec ompres sor are needed to see this pic ture. THE END Quic kTime™ and a dec ompres sor are needed to see this pic ture. Other Population increased