Risk Management
advertisement
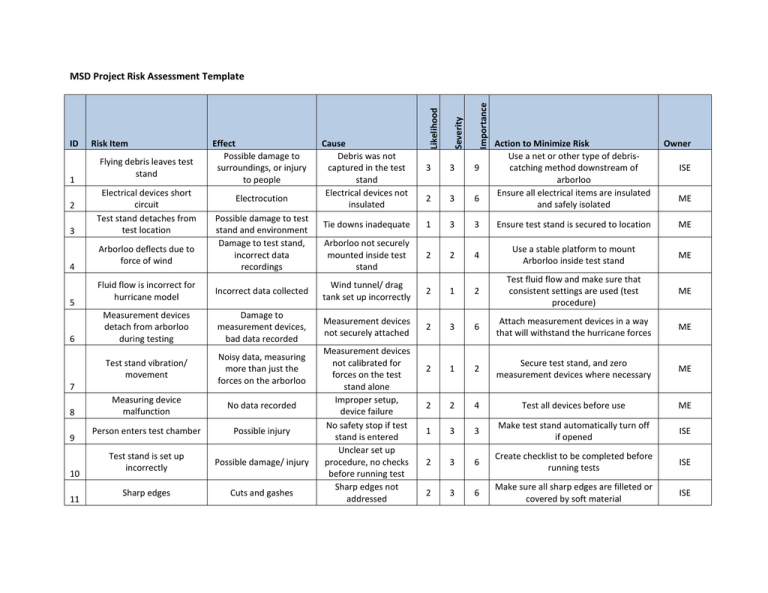
1 2 3 4 5 6 Flying debris leaves test stand Electrical devices short circuit Test stand detaches from test location Arborloo deflects due to force of wind 9 10 11 Electrocution Possible damage to test stand and environment Damage to test stand, incorrect data recordings Cause Debris was not captured in the test stand Electrical devices not insulated Action to Minimize Risk Use a net or other type of debriscatching method downstream of arborloo Ensure all electrical items are insulated and safely isolated Owner 3 3 9 ISE 2 3 6 Tie downs inadequate 1 3 3 Ensure test stand is secured to location ME Arborloo not securely mounted inside test stand 2 2 4 Use a stable platform to mount Arborloo inside test stand ME ME Fluid flow is incorrect for hurricane model Incorrect data collected Wind tunnel/ drag tank set up incorrectly 2 1 2 Test fluid flow and make sure that consistent settings are used (test procedure) ME Measurement devices detach from arborloo during testing Damage to measurement devices, bad data recorded Measurement devices not securely attached 2 3 6 Attach measurement devices in a way that will withstand the hurricane forces ME Test stand vibration/ movement Noisy data, measuring more than just the forces on the arborloo 2 1 2 Secure test stand, and zero measurement devices where necessary ME Measuring device malfunction No data recorded 2 2 4 Test all devices before use ME Person enters test chamber Possible injury 1 3 3 Make test stand automatically turn off if opened ISE Test stand is set up incorrectly Possible damage/ injury 2 3 6 Create checklist to be completed before running tests ISE Sharp edges Cuts and gashes 2 3 6 Make sure all sharp edges are filleted or covered by soft material ISE 7 8 Effect Possible damage to surroundings, or injury to people Importance Risk Item Severity ID Likelihood MSD Project Risk Assessment Template Measurement devices not calibrated for forces on the test stand alone Improper setup, device failure No safety stop if test stand is entered Unclear set up procedure, no checks before running test Sharp edges not addressed 1 3 6 Make sure all tripping hazards are noted and if possible, tie down or remove the obstacle ISE 3 2 6 Do not run tests for too long and make sure all equipment is adequately cooled ISE Not secured properly 1 2 2 Poor data Lack of CFD modeling 2 2 4 Unreliable results Lack of validation 2 3 6 Sensors unreliable Varying results Cheap sensors 1 3 3 Air gets through barb holes Pressure distribution incorrect Holes not sealed 2 3 6 Wires obstruct air flow Air flow will be disturbed 2 2 4 Overloading load sensor Damage to sensor 2 3 6 Pressure range exceeds the range for the sensors No data collection Tripping hazards Possible injury and damage to equipment Equipment overheating Damage to equipment Parts fall off in wind tunnel Damage to wind tunnel 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Wind Speeds do not meet requirements Assumptions on coefficient of drag incorrect 24 25 26 Poor wire management Limits of sensor not adhered to Assumptions about pressure range are wrong User breaking equipment Parts not fitting together 23 Tripping hazards not recognized and mitigated Equipment run for too long or not adequately cooled Assembly can't be completed and parts would need to be remade Drawings are subject to measurement error Ensure all equipment is properly secured Run simulations to ensure we are collecting proper data Verify all calculations are correct with professors and experts ME Test sensors before use on model ISE/ME Verify seals, if necessary apply another gasket Secure wires and run them away from critical areas Apply a safety margin to avoid overloading sensor ISE ME ME ME ME 2 ME 1 ISE/ME 2 3 6 ME Likelihood scale 1 - This cause is unlikely to happen 2 - This cause could conceivably happen 3 - This cause is very likely to happen Severity scale 1 - The impact on the project is very minor. We will still meet deliverables on time and within budget, but it will cause extra work 2 - The impact on the project is noticeable. We will deliver reduced functionality, go over budget, or fail to meet some of our Engineering Specifications. 3 - The impact on the project is severe. We will not be able to deliver, or what we deliver will not meet the customer's needs. “Importance Score” (Likelihood x Severity) – use this to guide your preference for a risk management strategy Prevent Action will be taken to prevent the cause(s) from occurring in the first place. Reduce Action will be taken to reduce the likelihood of the cause and/or the severity of the effect on the project, should the cause occur Transfer Action will be taken to transfer the risk to something else. Insurance is an example of this. You purchase an insurance policy that contractually binds an insurance company to pay for your loss in the event of accident. This transfers the financial consequences of the accident to someone else. Your car is still a wreck, of course. Accept Low importance risks may not justify any action at all. If they happen, you simply accept the consequences.