Chapter 7 Marketing Research and Decision Support Systems
advertisement

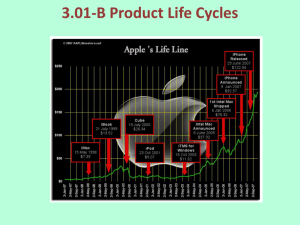
Developing and Managing Products Chapter 11 “When you innovate, you’ve got to be prepared for everyone telling you you’re nuts.” Larry Ellison, Founder Oracle Corporation 2 http://www.achievement.org/autodoc/page/ell0bio-1 First flight! Dec. 17th 1903, Orville at the controls, 12 seconds, 120 feet. 3 How do we create value through innovation? Over half of all growth in the United States comes from new products and services The greatest rewards go to companies that create new business models First mover advantage And we are happy-..er… Types of innovations ……………innovations - normal upgrading, no change in user behaviors. New to the market New to seller New to producer ………………..innovations/Destructive creation – require users to change behaviors. New-to-the-world products. New Product Development Process 4. ................... 5. ……….marketing 3. Business Analysis Alternative versions, describe in consumer terms 6. Commercialization 2. ........... Screening Reduce # quickly 1. Idea Generation By many -- employees, customers, suppliers, distributors, competitors Physical product, $$$ New Product Development Process 2. Idea Screening (what do we have? +/-) • In pharmacy, 1 of 5,000 new drug ideas is common • In autos, 1 of 20 new car concepts is made to prototype • Point? Brainstorm, then cut via research • Short and long run $ performance • Social issues: • Consumer welfare (Ben and Jerry’s) • Safety ( Marlboro cigarettes) – liability (McDonald’s hot coffee) New Product Development Process 3. Business Analysis • Examine consumer perceptions • Consider view of retailers and wholesaler 4. Development (can go hand-in-hand with analysis) • Product tests (New Coke, movies) • Risky: (leaks, skewed results) • Virtual product development: examine without construction • Prototype product and marketing strategy • Longest process (Minute Rice took 18 years!) Concept Test Concept Test A test to evaluate a new-product idea, usually before any prototype has been created. Test Marketing +Costs +Brand Equity -Jamming -Duplication Standard Test Market Limited introduction in a small market supported by a full-fledged marketing campaign to gauge customer reactions Product Life Cycle:PLC A concept that provides a way to trace the stages of a product’s acceptance, from its introduction (birth) to its decline (death). Product Life Cycles Introduction ………… ………….. Decline Dollars Industry ……….. Industry ………. 0 Time Product Life Cycles Strategies INTRODUCTION Sales Product Strategy Limited models Frequent changes GROWTH More models Frequent changes. MATURITY Large number Eliminate of models. unprofitable models Distribution Strategy Limited Expanded Wholesale/ dealers. Longretail distributors term relations Extensive. Margins drop. Shelf space Promotion Strategy Awareness. Aggressive ads. Stimulate Stimulate demand.Sampling demand Advertise. Promote heavily Pricing Strategy High to recoup development costs Fall as result of competition & efficient production. Time DECLINE Prices fall (usually). Phase out unprofitable outlets Phase out promotion Prices stabilize at low level. Examples INTRODUCTION GROWTH MATURITY DECLINE Third generation mobile phones Transition lenses Personal Computers Typewriters E-conferencing Email Faxes Handwritten letters All-in-one racing skin-suits Breathable synthetic fabrics Beer, Autos VCR iris-based personal identity cards Smart cards Credit cards Cheque books Some misconceptions about PLC At the level of the category and not the brand – Cell phones not CINGULAR wireless. However, in practice is used both ways.. Different products go through the stages differently. Timing of stages may vary substantially. What other advantages do you see for a M. Manager? Product Life Cycles INTRODUCTION Sales Product Strategy Limited models Frequent changes GROWTH More models Frequent changes. Distribution Strategy Limited Expanded Wholesale/ dealers. Longretail distributors term relations Promotion Strategy Awareness. Aggressive ads. Stimulate Stimulate demand.Sampling demand Pricing Strategy High to recoup development costs Fall as result of competition & efficient production. Time MATURITY DECLINE Large number Eliminate of models. unprofitable models Extensive. Margins drop. Shelf space Advertise. Promote heavily Prices fall (usually). Phase out unprofitable outlets Phase out promotion Prices stabilize at low level. Extending the PLC Change product Change product use Change product image Change product positioning What already presented tool can help us out here? Product Life Cycle Factors that may speed products through PLC: 1. 2. 3. 4. Ease of trial Ease of use Easy to communicate advantages Compatible with customer experience The Consumer Adoption Process Adoption process: series of stages for which consumers decide whether or not to become a regular user of a new product, including: Awareness Interest Evaluation Trial Adoption or rejection Diffusion Diffusion The process by which the ………….of an innovation spreads. Adopter Categories …. …. Diffusion Process and PLC Curve Introduction Growth Decline Maturity Sales Product life cycle curve Early majority Late majority Early adopters Innovators Laggards Diffusion curve How do we use the Diffusion of innovation theory? - MM can predict which types of customers will buy their products immediately after introduction or later Can develop effective MMix Product Characteristics and the Rate of Adoption Complexity Compatibility Relative Advantage Observability Trialability