Cell Type Note Sheet
advertisement
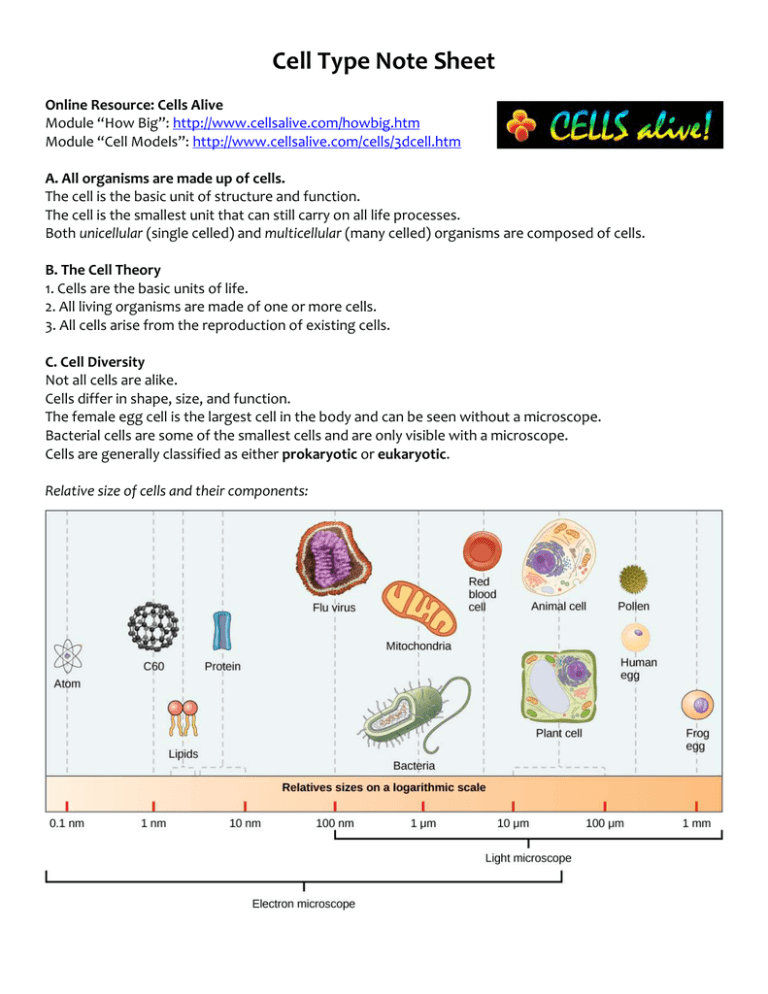
Cell Type Note Sheet Online Resource: Cells Alive Module “How Big”: http://www.cellsalive.com/howbig.htm Module “Cell Models”: http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/3dcell.htm A. All organisms are made up of cells. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. The cell is the smallest unit that can still carry on all life processes. Both unicellular (single celled) and multicellular (many celled) organisms are composed of cells. B. The Cell Theory 1. Cells are the basic units of life. 2. All living organisms are made of one or more cells. 3. All cells arise from the reproduction of existing cells. C. Cell Diversity Not all cells are alike. Cells differ in shape, size, and function. The female egg cell is the largest cell in the body and can be seen without a microscope. Bacterial cells are some of the smallest cells and are only visible with a microscope. Cells are generally classified as either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Relative size of cells and their components: D. Cell Commonalities ALL CELLS (both prokaryotic and eukaryotic) contain the following… 1. Plasma Membrane (aka cell membrane): This membrane functions to separate the interior of the cell from the exterior environments and regulates the entry and exit of materials from the cell. 2. DNA: The nucleic acid that serves as the inherited information of the cell and directs cellular processes. In prokaryotes, the cell’s circular DNA is found free floating in the nucleoid region of the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, the linear DNA is packaged within a membrane-bound nucleus. 3. Cytoplasm: The gel-like substance of a cell, containing an aqueous suspension of all the cell components. 4. Ribosomes: The site of protein synthesis. PROKARYOTES a. Prokaryotic cells are less complex and usually unicellular. b. Prokaryotes do NOT have a nucleus or any other membranebound organelles. c. Most have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane and a single, looped piece of DNA in the nucleoid region of the cytoplasm (NOT within a nucleus!). d. Prokaryotic cell types include bacteria and Archaea. EUKARYOTES a. Eukaryotic cells are more complex. b. Can be both unicellular and multicellular organisms. c. Eukaryotes have a nucleus and other membranebound organelles. d. Membrane-bound organelles are internal structures in the cells that perform specific functions, and which are enclosed by either a single or double membrane. e. The nucleus is located in the center of the cell and contains the genetic material (DNA). It controls the activities of the cell. f. Eukaryotes include plant cells, animal cells, fungi, algae, and protists. Chloroplast Mitochondrion Golgi Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Comparing animals cells vs. plant cells… Animal Cell Plant Cell Cell Shape Round and irregular Rectangular, fixed shape Cell (Plasma) Membrane Present Present Cell Wall Absent Absent Vacuole One or more small vacuoles One, large, central vacuole taking up 90% of cell volume (for water storage). Centrioles Present in all animal cells. Only present in lower plant forms. Chloroplast Absent Present (for photosynthesis – plants are autotrophs) Cytoplasm Present Present Endoplasmic Reticulum Present Present Ribosomes Present (protein synthesis) Present (protein synthesis) Mitochondria Present (cell respiration) Present Golgi Apparatus Present Present Microtubules/ Microfilaments Present Present Flagella May be found in some cells May be found in some cells Lysosomes Present ( have digestive enzymes) Not usually present Nucleus Present (holds DNA) Present (holds DNA) Cilia Present Very rare








