Fire Safety & Fire Extinguisher Use
advertisement

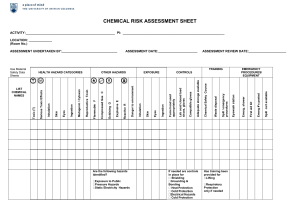
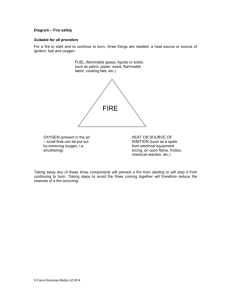
Fire Risk Assessment How Does a Fire Work? • Three components • Need all three components to start a fire • Fire extinguishers remove one or more of the components The Five Steps of Fire Risk Assessment • Step 1 – Identify the Fire Hazards. • Step 2 – Who could be in danger. • Step 3 – Examine the existing precautions and re-evaluate their effectiveness. • Step 4 – Record the findings. • Step 5 – Review and revise the assessment. Step 1 – Identify the Fire Hazards For fire Heat, Fuel & Oxygen are needed. Common Sources of Heat •Smoking Materials, Naked Flames, Heaters, Welding, Grinding, Engines, Machinery, Faulty Electrical Equipment, Lights & Lighting Equipment, Hot Surfaces, Friction, Static, Metal Impact, Arson etc. Look for potential near misses indicated by scorch marks, cigarette burns or discoloured plugs or sockets. Step 1 – Identify the Fire Hazards For fire Heat, Fuel & Oxygen are needed. Common Sources Of Fuel •Paints, Varnish, Thinners, Adhesives, Petrol, White Spirit, Methylated Spirit, Paraffin, Chemicals, Wood, Paper, Plastic, Rubber, Foam, Furniture, Waste Materials etc. Step 1 – Identify the Fire Hazards For fire Heat, Fuel & Oxygen are needed. Sources Of Oxygen •The air around us. •Oxidising Chemicals •Oxygen Cylinders The main supply of air to a fire is usually the air that is around us and the fire is encouraged to grow by airflow though doors, windows and other openings Step 1 – Identify the Fire Hazards Heat Fuel Oxygen Step 2 – Who Could Be In Danger Questions to ask yourself are, •Who is at risk. •In the event of a fire how can they be warned. •How will they escape or reach a place of safety. As well as people at their normal place of work do not forget to include visitors, contractors and members of the general public who may be on site. Remember always to consider any special requirements that may be needed for escape for example by disabled people. Step 3 – Examine the Existing Precautions & Re-evaluate Their Effectiveness Once the hazards and the people at risk have been identified then the next step is to consider if the precautions in place are adequate and can the risks be reduced further. Ask the following questions, •Are there any sources of heat that can be removed and replaced with a safer alternative. •Are sources of heat being used as per the manufacturers instructions and are they being properly maintained. •Has machinery been installed that is designed to minimise the risk of fire and explosion. •Have naked flame and radiant heaters been replaced by convector heaters or central heating systems. Step 3 – Examine the Existing Precautions & Re-evaluate Their Effectiveness •Are electrical fuses and circuit breakers correctly rated. •Is there any overloaded electrical or mechanical equipment. •Are all ducts and flues regularly cleaned. •When carrying out hot work is there a permit to work system in operation. •Is there a no smoking policy with a ban on smoking or designated smoking areas clearly defined. •Are regular inspections of the workplace undertaken to ensure that there is no accumulation of rubbish and to help prevent the risk of arson. •Are flammable materials kept to a minimum and are these stored safely. •Can flammable materials that are being used be replaced by less flammable or non-flammable substitutes. Step 3 – Examine the Existing Precautions & Re-evaluate Their Effectiveness •Have wall and ceiling linings where possible been treated to reduce the rate of flame spread across the services. Step 4 – Record the Findings •Once the risks and the control measures have been identified, a simple method of recording these findings is required. •The next slide shows a typical risk assessment and the key things to notice are that the hazard and control measures are assessed and any remedial measures needed are recorded and a timescale with responsibility set for completion. Step 4 – Record the Findings Step 5 – Review & Revise The Assessment •The risk assessment will have highlighted improvements and remedial measures to be carried out. •A review is necessary to ensure that these tasks have been completed. •A review is also required if there are any changes in the workplace such as new plant and equipment, changes to buildings, work processes, number of people present etc.