1_1 1400-1763
advertisement
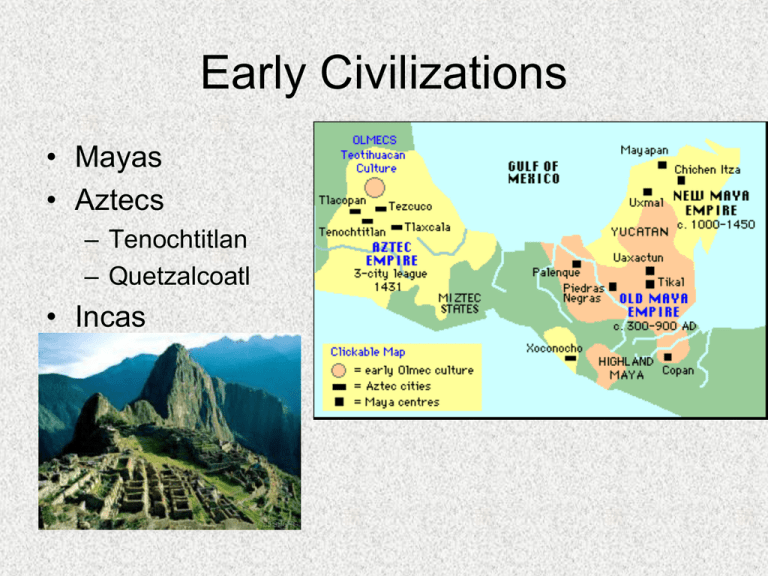
Early Civilizations • Mayas • Aztecs – Tenochtitlan – Quetzalcoatl • Incas North American cultures • • • • Climate determines Matrilineal Shaman Communal ownership Cultural Exchange • From New World – Buffalo, iguanas, rattle snakes – Tobacco, corn, beans, tomatoes, potatoes – syphilis • From Old World – Cattle, pigs, goats, horse – Weeds – Small pox, malaria, yellow fever European Developments • Political changes – – – – – Portugal Spain England France Holland European Developments (cont’d) • Shipbuilding and Navigation – – – – Caravel Compass Astrolabe Portolano European Developments (cont’d) • Religious motive – Catholics vs. Protestants – Reformation • Wealth – Northwest Passage Shift from Medieval to Early Modern Europe • Crusades • Renaissance • Reformation – – – – – Hus, Wycliffe Luther Gutenberg Calvin Henry VIII Exploration • Vikings – Eric the Red – Leif Ericson – Vinland Exploration • Portugal – Prince Henry – Dias – Vasco da Gama Exploration • • • • Columbus Cabral Vespucci Line of Demarcation – Alexander VI • Treaty of Tordesillas 1481 Bull Aeterni regis "all lands south of the Canary Islands belongs to Portugal." 1493 Bull Inter caetera "all lands east of 38° west longitude belongs to Portugal and those west of that belong to Spain." 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas "The pope's line of 1493 is moved to 46° 37'.” Exploration-Spanish • Balboa • Magellan • Cortes Pizarro Coronado De Soto Ponce de Leon Other explorers • English – – – – John Cabot Sebastian Cabot Drake Frobisher • French – Verrazano – Cartier – Champlain • Dutch – Hudson European Voyages of Discovery in the Atlantic in the Fifteenth and Sixteenth Centuries Spanish, English, and French Settlements in North America in the Sixteenth Century Spain’s Colonization • • • • • Conquistadors Ruled from home Short time Encomiendas Riches (next slide) Value of New World Treasure Imported into Spain, 1506–1655 Early Colonization • Hispaniola • Carolinas to Florida • St. Augustine 1565 European Colonization • French – Huguenots – Missionaries – Fur trade • Dutch – West India Company – Ft. Orange – New Netherlands English Colonization • Roanoke Island – Virginia Dare – CROATOAN • Joint Stock – London Company – Plymouth Company • Covenant • Proprietary • Royal Jamestown • • • • • John Smith Powhatan John Rolfe House of Burgesses Indentured Servants The London Company, 1606 Jamestown Settlement, 1609 Chesapeake Bay Jamestown Settlement Jamestown Housing Jamestown Chapel, 1611 Jamestown Fort, 1609 Jamestown Settlement (Computer Generated) Captain John Smith English Migration: 1610-1660 Headright System Jamestown Colonization Pattern: 1620-1660 John Rolfe Tobacco Plant Early Colonial Tobacco 1618 — Virginia produces 20,000 pounds of tobacco. 1622 — Despite losing nearly one-third of its colonists in an Indian attack, Virginia produces 60,000 pounds of tobacco. 1627 — Virginia produces 500,000 pounds of tobacco. 1629 — Virginia produces 1,500,000 pounds of tobacco. Tobacco Prices: 1618-1710 Indentured Servitude Chief Powhatan Pocahontas Powhatan Confederacy Powhatan Indian Village Indian Foods Native American Population in North America Why was 1619 a pivotal year for the Chesapeake settlement? Virginia House of Burgesses 17c Population in the Chesapeake 100000 80000 60000 White 40000 Black 20000 0 1607 1630 1650 1670 1690 Population of Chesapeake Colonies: 1610-1750 Virginia Colony • William Berkeley • Bacon’s Rebellion Governor Berkeley’s “Fault Line” Colonization of Maryland Maryland • George Calvert – 1st Lord Baltimore • Cecilius Calvert – 2nd Lord Baltimore • Act of Toleration Plymouth The Mayflower Compact November 11, 1620 The Mayflower • Miles Standish • William Bradford • 1625-1691 Pilgrims? vs. Puritans? Massachusetts Bay Colony • Puritans • Harvard • John Winthrop We shall be as a city on a hill.. •Great Migration –John Cotton –Thomas Hooker Sources of Puritan Migration Rhode Island • Roger Williams – Separation of church and state • Anne Hutchinson Connecticut • Hooker • Fundamental Orders • New Haven Others from Massachusetts • New Hampshire • Maine Colonizing New England Land Division in Sudbury, MA: 1639-1656 NE Governments and Trade • • • • • • • More democratic Bicameral Town meetings Triangular trade Small farms Fishing shipping Puritans fall • • • • • • Charles I Oliver Cromwell Charles II Half-way Covenant Secular Salem Attempts at Unification The Pequot Wars: 1636-1637 A Pequot Village Destroyed, 1637 • New England Confederation • Religious minorities Restoration to Glorious Revolution • New Haven • Maine • Edmund Andros King Philip’s War • Wampanoags • Narragansett Campaign • Philip betrayed Dominion of New England • • • • • • New Hampshire Andros Increase Mather Cotton Mather Glorious Revolution William and Mary Population of the New England Colonies Population Comparisons: New England v. the Chesapeake New England Colonies, 1650 New Netherlands • Dutch West India Company • Peter Minuit • New Sweden • New Amsterdam • Peter Stuyvesant • Patroonships In 1625 he went to the Netherlands. Appointed a director of the Dutch West India Co., he set out for the company's settlement in America. He reached Manhattan Island in 1626 and purchased it from the Indians with trinkets valued at the amount of 60 guilders, or about $24. Because of differences with the company, he was recalled in 1631. In 1637 he set out to form a Swedish colony in America and in 1638 built Fort Christina (now Wilmington, Del.). New York Manors & Land Grants Patroonships Settling the Middle [or “Restoration”] Colonies New Netherlands & New Sweden New York Harbor, 1639 New York • • • • Charles II James Anglo-Dutch Wars Leisler’s Rebellion New Jersey • John Lord Berkeley • George Carteret • East and West Jersey Royal Land Grant to The “Holy Pennsylvania Experiment” Penn • William Penn • Quakers – Equality, simplicity, peace Penn & Native Americans Penn’s Treaty with the Native Americans Delaware Carolinas • 8 proprietors • Fundamental constitutions • Culpepper rebellion • North and South Berkeley Georgia • James Oglethorpe • Buffer • Debtors Urban Population Growth 1650 - 1775 Ethnic Groups Struggle for Empire • • • • Mercantilism Objectives Enclosure Movement Adam Smith, Wealth of Nations Early Attempts at Mercantilism • • • • • • • • Navigation Acts Act of Fraud Enumerated goods Wool Act Hat Act Molasses Act Iron Acts Salutary Neglect Enforcement of Navigation Laws • • • • • • Privy Council Lords of Trade Sec. of State Board of Trade Treasury Board Vice-Admiralty Courts English Government beliefs • Divine Right • Virtual Representation • Limited Suffrage • Unwritten Constitution • Anglican Church • Basic English Rights Magna Carta Colonial Government • • • • • • • Royal Governor Council Assembly Power of the Purse Actual representation Frontier vs. Coast Division between colonies Colonial Changes-Religion • Tax supported • England’s Act of Toleration • MA, NH, CN had established churches still at Revolution NH MA CN Anglo-French Relations • • • • • Fishing Fur trade Acadia Mississippi Hudson Bay Anglo-French Wars • King William’s War • Queen Anne’s War – War of Jenkin’s Ear • King George’s War • Seven Years War (French and Indian War) French and Indian War • Fort Duquesne – Washington – Fort Necessity • • • • Albany Congress William Pitt Quebec Treaty of Paris







