Urban Land Models - My Teacher Pages
advertisement
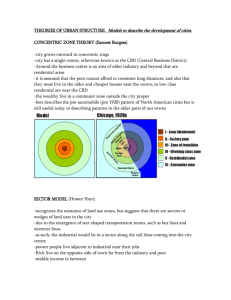
Urban Land Models AP Human Geography Russellville High School What do we always say about models? This is a model Is this what real women look like? It’s the same way with models in geography… Geography models are simply representations of the built environment What do we always say about models? Most importantly – they are just models Models only represent patterns in space The landscape does NOT look exactly like the model Models are thus representations of the landscape to help better understand patterns Three Classic Urban Models Other Urban Models Burgess Concentric Zone Model http://www.lgfl.net/lgfl/leas/barnet/accounts/migration/web/Land%20Use/documents/burgess-re-done.jpg Characteristics of Concentric Zone en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ernest_Burgess Burgess studied 1920s Chicago to make this model 5 concentric zones Burgess suggested that immigrants lived in inner zones which caused affluent residents to move farther out Invasion and Succession Concentric Zone’s weakness is that it does not allow for change in the city Concentric Zone does not allow for physical geographic barriers Or, how about this? Pg. 411 Rubenstein Applying the Models Look at the map (figure 13-7) of Dallas on Page 413 of Rubenstein for Concentric Zone Look at the map (figure 13-8) of Dallas on Page 413 of Rubenstein for Sector Model Look at the map (figure 13-9) of Dallas on Page 414 of Rubenstein for Multiple Nuclei Compare with Dallas map on Page 422 Does this really work on the landscape? Hoyt Sector Model Hoyt Sector Model Late 1930s Answered the drawbacks of Burgess Model Hoyt said growth created pie-shaped urban structure Hoyt said his pie-shaped zones could reach from the Core (CBD) to the edge of the city (e.g. low rent sector 3 from CBD to outskirt of city) Sector Model says that the CBD is not as important as Burgess indicated Sectors were developed along transport routes (e.g. highways, RRs, etc.) Or, how about this? Pg. 411 Rubenstein Harris & Ullman – Multiple Nuclei http://cronodon.com/PlanetTech/Cities_Structure.html Multiple Nuclei 1940s Harris & Ullman hypothesized the CBD was further losing its dominance CBD no longer the nucleus of the modern city, thus emergence of ‘nuclei’ Reflects decentralization and then re-nucleation of urban functions Nuclei are disconnected and do not necessarily rely on each other Or, how about this? Pg. 412 Rubenstein Let’s look at all three now www.csiss.org Urban Realms Model www.csiss.org Hartshorn and Mueller 1980s Modeled after cities like Atlanta and Los Angeles Further metamorphosis of multiple nuclei World City Models Latin American City Model http://lewishistoricalsociety.com/wiki2011/tiki-read_article.php?articleId=96 World City Models Southeast Asian City Model http://lewishistoricalsociety.com/wiki2011/tiki-read_article.php?articleId=90 World City Models African City Model Favela in Rio de Janiero http://getmobetter.wordpress.com/2009/10/09/the-real-rio/ Slums, Squatter Settlements in Nairobi, Kenya http://www.nowpublic.com/environment/nairobis-slums Urban Issues – Segregation – Where are Cubs and White Sox fans? http://www.thechicago77.com/2009/01/chicago-is-americas-most-segregated-city/ CITYSCAPES – What are they? Chicago Seattle St. Louis Shanghai London New York City Paris Athens Urban Terms Rank-Size Rule Bedroom Communities Sense of Place In-fill or In-filling Covenants Zoning NIMBY Revitalization Gentrification DINK Commodification Blockbusting Redlining Other Side of the Tracks Tenements/Row Houses/Brownstones White Flight Edge Cities Megalopolis Another way to keep “those people” out Zoning Transportation geography – creating highways, rails as buffers between racial areas Suburbs – property values Creation of parks to block development Deerfield, IL case study Let’s look at all three now