Pleural ,peritoneal, pericardial and synovial fluids culture
advertisement

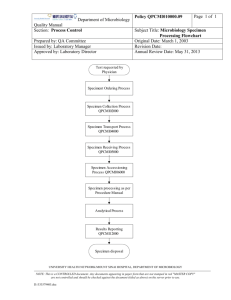
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم 2013-2014 L/O/G/O Diagnostic Medical Microbiology-Laboratory Manual Body Fluid Culture Aim of the test Isolate and identify pathogenic organisms from normally sterile body fluids and perform sensitivity test Types of specimen Aseptically aspirated body fluid (e.g., , synovial, peritoneal fluid). Criteria of specimen rejection Inappropriate specimen transport device; mislabeled specimen; unlabeled specimen; specimen received after prolonged delay (usually more than two hour); specimen received in expired transport media. Infection Of Sterile Body Fluid all body fluid are sterile Common Pathogenic of Precarditis And Myocarditis Mycoplasma pneumoniae Chlamydia trachomatis Mycobacterium tuberculosis Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus pneumoniae Enterobacteriacae and other gram negative Bacilli Fungi Pleural Fluid Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Enterobacteriacae Pseudomonas spp. Anaerobic bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis Coccidoides immitis Actinomyces spp. Aspergillus spp. Candida spp. Cryptococcus neoformans Histoplasma capsulatum Bones and joints Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus pyogenes Haemophilus influenzae Streptococcus pneumoniae Enterobacteriacae Mycobacterium spp Neisseria gonorrheae Peritoneal fluid Streptococcus pneumoniae Group A streptococci Enterobacteriacae Other gram negative bacilli Staphylococci Neisseria gonorrheae Chlamydia trachomatis Fungi Coccioides immitis Candida spp Pre specimen processing Who will collect the specimen Physician Quantity of specimen 1-5 mL is adequate, a larger quantity of fluid is better. Time relapse before processing the sample Body fluids should be treated as CSF specimens and should processed immediately. Storage Maintain specimen at room temperature. Do not refrigerate. Specimen processing Specimen processing Body fluids for culture should be concentrated by either filtration or high speed centrifugation. Filtration of fluid through a 0.45 micrometer poresize membrane filter allows a greater volume of fluid to be processed and usually yield better results, then the filter should be cut aseptically into pieces, one of which is placed on chocolate agar for incubation in 5% carbon dioxide, one on MacConkey agar, on blood agar plate for aerobic incubation, and the last on a blood agar plate for anaerobic incubation. Specimen processing If fluid has been concentrated by centrifugation, the resulting sediment should be inoculated to an enrichment broth, blood, chocolate and MacConkey agars. All fluids should be processed for direct microscopic examination, in general if one organism is seen per oil immersion field at least 105 organisms per milliliter of specimen are present. Specimens for fungi should be examined by direct wet preparation or by preparing 10% KOH for visualization of fungi element from a wet preparation. Acid Fast stain for Mycobacterium spp. Post specimen processing Interfering factors: Patient on antibiotic therapy. Improper sample collection. Result reporting: Report Gram stain, KOH, and AFS finding as an initial report. Report the isolated pathogen and its sensitivity pattern as a final report. Turn around time: Gram stain and wet mount results should be available 1 hour after specimen receipt. Isolation of a possible pathogen can be expected after 2-4 days. Negative culture will be reported out 1-2 days after the receipt of the specimen. L/O/G/O Any Questions ?