4.6
advertisement

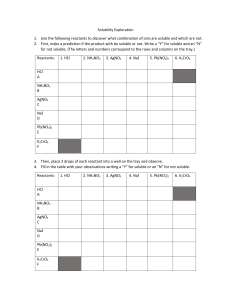
3.4 Double Displacement Reactions Double Displacement Reactions • Double Displacement Reactions occur when a metal replaces a metal in a compound and a nonmetal replaces a nonmetal in a compound • Compound + compound product + product • AB + CD AD + CB Double Displacement Reactions • Think about it like “foil”ing in algebra, first and last ions go together + inside ions go together • Example: AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(s) AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq) • Another example: K2SO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) 2 KNO3(aq) + BaSO4(s) Solubility of D.D. Products A property of a substance that describes it’s ability to dissolve in another substance at a given temperature and pressure The solute is the substance that is dissolved The solvent is the medium in which the solute dissolves If the product of a reaction is very soluble and will stay in solution it may be given the subscript (aq) A product that is insoluble is given the subscript (s) or (g) depending on it’s state when produced A solid, undissolved product is a precipitate Solubility Predictions Use Table 1 p. 173 to predict whether an ionic compound, formed as the product of a chemical redaction in solution, is likely to form a precipitate (not soluble) or form a solution (soluble) If both possible products are highly soluble, write “no reaction” Practice • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Predict the products. Balance the equation HCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) HNO3(aq) + AgCl(s) 3CaCl 2(aq) + 2Na3PO4(aq) Ca3(PO4)2(s) + 6NaCl(aq) Pb(NO3)2(aq) + BaCl2(aq) PbCl2(s) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) FeCl3(aq) + 3 NaOH(aq) FeOH3(s) + 3NaCl(aq) H2SO4(aq) +2NaOH(aq) H2O(l) + Na2SO4(aq) 2KOH(aq) + CuSO4(aq) Cu(OH)2(s) + K2SO4(aq) Types of Double Displacement Reactions Precipitate Reactions – one of the two products is an insoluble product The other product may remain in solution AgNO3(aq) + KCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq) Reactions Producing a Gas – One of the products is a gas which is released Na2S(aq) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2S(g) See table 2 p. 176 for more examples of gases Neutralization Reaction – reaction between an acid and base where water and a salt (ionic compound) are produced HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) Mixed Practice • 1. 2. 3. 4. State the type, predict the products, and balance the following reactions: BaCl2 + H2SO4 2HCl + BaSO4 D.D S.D Zn + CuSO4 ZnSO4 + Cu 2 Cs + 3 Br2 2CsBr3 Synthesis Decomposition FeCO3 Fe + CO 3 Homework Read pp. 172 – 177 Answer p.177 # 4 – 6