THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AP BIOLOGY MS. VITALE •LYMPATIC
advertisement

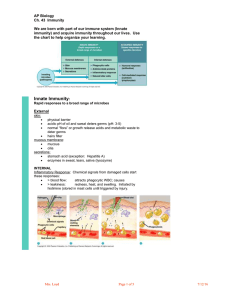
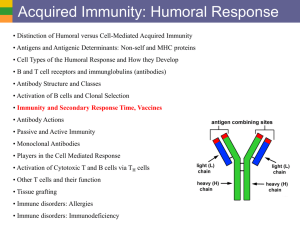
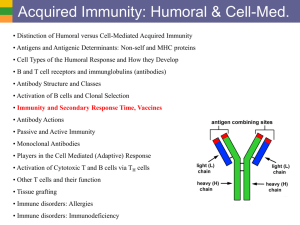
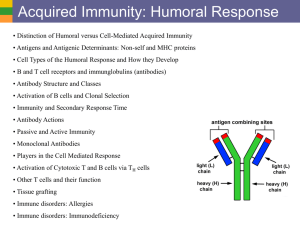
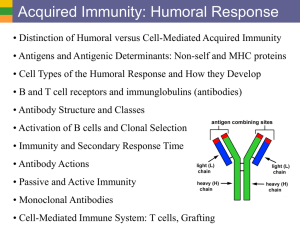
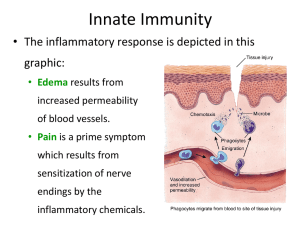
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AP BIOLOGY MS. VITALE •LYMPATIC SYSTEM •Lymphatic vessels -Pick up excess fluid and return to blood stream •Lymph nodes -Remove foreign material from lymph -produce lymphocytes (immunity) •Macrophages- engulf and destroy foreign material •lymphocytes-(WBC)- respond to foreign substances •SPLEEN •Filters blood •Cleanses blood •Destroys RBCs •Stores platelets and blood •THYMUS GLAND •Peaks during youth •Above heart •Produces hormones for immunity •TONSILS •Throat •Removes pathogens •PEYER’S PATCHES •Small intestine •Capture bacteria THE IMMUNE SYSTEM •THE BODY DEFENDS ITSELF IN TWO WAYS •Nonspecific (immediatate) •Specific (The immune system) •NONSPECIFIC BODY DEFENSES •Pathogens- disease causing agents •First line of defense •Skin secretions •Sebum •Stomach •Lysozyme •Mucus •Second line of defense •Phagocytes -engulf foreign material via endocytosis •Natural killer cells -lyse and kill cancer cells and virus-infected cells -release perforins which lyse cell membrane •INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE •Redness, heat, swelling, pain •injured cells release histamines and kinins •Blood vessels dialate •Pain receptors activated •Attract phagocytes and WBCs -The inflammatory response: 1. prevents spread of damaging agents 2. disposes of debris and pathogens 3. sets the stage for repair •COMPLEMENT PROTEINS •Over 20 •Attaches to foreign cell and is activated •Produces lesions •Amplifies inflammation •Releases vasodialators and chemotaxis chemicals •INTERFERON •Secreted by virus infected cells •Diffuses into nearby cells and protects •FEVER •Can be beneficial •Bacteria need iron and zinc •Fever makes them unavailable •Increases metabolism them from virus •SPECIFIC BODY DEFENSES: THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 1.Antigen specific -recognizes and acts against particular pathogens or foreign substances 2.Systemic -not restricted to the initial infection site 3.Has memory -recognizes and mounts even stronger attacks second time •TWO TYPES OF IMMUNITY •Humoral immunity (antibodies) •Cell-mediated immunity (lymphoctes) -virus infected cells, cancer cells, transplants -lymphocyte lyses cell •ANTIGENS •Provoke immune response •Nonself •CRUCIAL CELLS •Lymphocytes -B cells produce antibodies -T cells are non-anti-body producing -involve cell mediated immunity •Macrophages •LYMPHOCYTES •Hemocytoblasts in bone marrow •T cells arise in thymus •B cells arise in bone marrow •MACROPHAGES •Form from monocytes in red bone marrow •Non-specific •Present fragments of antigen on their surface •Recognized by T cells •Secrete monokines •T cells release chemicals that cause macrophages to become killers •HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE •When a B cell binds to an antigen, clonal selection is activated -B cells grow and multiply producing clones •Primary humoral response -production of clones •most clones become Plasma cells -produce specific antibody •other clones become Memory cells -live longer and respond later in Secondary humoral response •ACTIVE IMMUNITY -B cells encounter antigens and produce antibodies •Naturally acquired active immunity (have infection) •Artificially acquired active immunity (vaccine) •PASSIVE IMMUNITY -antibodies received from serum of immune individual -Borrowed antibodies -from mother -serum from another •COMMERCIAL USE •Monoclonal antibodies cultivated from single cell •Deliver cancer-fighting drugs •Diagnose pregnancy, hepatitis, rabies •ANTIBODIES Immunoglobins (Igs) 4 AA chains Heavy chains Light chains Variable region Constant region Antigen-binding site •ANTIBODY CLASSES Antibodies inactivate antigens in a number of ways: 1. COMPLEMENT FIXATION (most important) -Vs. bacteria and mismatched RBCs -Triggers lysis -Enhances inflammation 2. NEUTRALIZATION •Antibody binds to site on exotoxin or virus •Blocks effect 3. AGGLUTINATION •Antibody binds to more then one antigen •Causes clumping •Basis for blood typing tests 4. PRECIPITATION •Cross-linking involves soluble antigens •Precipitate out •Complexes are phagocytized •CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE •HELPER T CELLS •SUPPRESSOR T CELLS and MEMORY CELLS •ORGAN TRANSPLANTS 1.Autografts 2.Isografts 3.Allografts 4.Xenografts •MATCHING •Blood and cell membrane antigens •Immunosuppressive therapy •ALLERGIES •Abnormal immune response •Allergen •Immediate or acute •ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK •IMMUNODEFICIENCIES •Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease •AIDS •AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES •Multiple sclerosis •Myasthenia gravis •Graves disease •Type 1 diabetes •Lupus •Rheumatoid arthritis