The Carbon Cycle - Science at NESS
advertisement
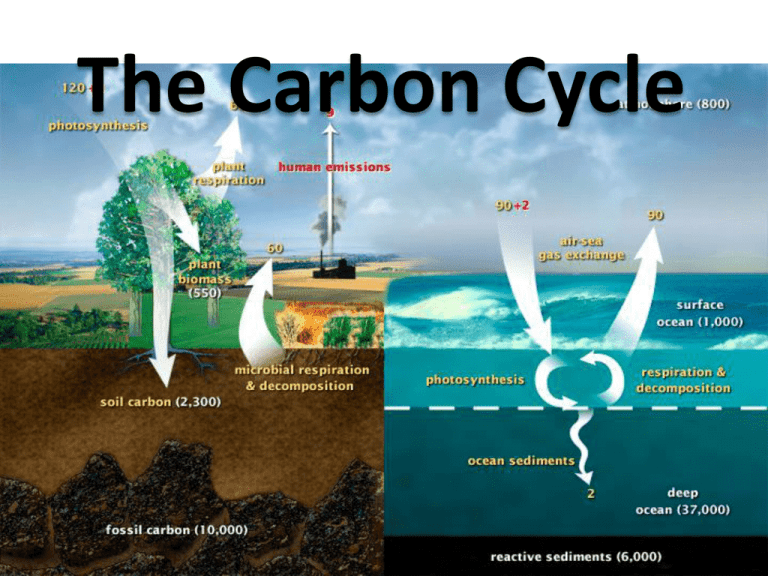
The Carbon Cycle The Carbon Cycle Science 10 Data Booklet Shows Three Parts to the cycle 1) Cycling Carbon: The carbon that is moving through the ecosystem Science 10 Data Booklet Shows Three Parts to the cycle 1) Cycling Carbon: The carbon that is moving through the ecosystem 2) Stored Carbon: The carbon that is not available Science 10 Data Booklet Shows Three Parts to the cycle 1) Cycling Carbon: The carbon that is moving through the ecosystem 2) Stored Carbon: The carbon that is not available 3) Carbon exchange: The trade off. How much is going in and how much is going out of a store Science 10 Data Booklet Cycling carbon comes in four pathways 1) Photosynthesis: Plants use carbon dioxide and water to make sugar and oxygen CO2 + H2O -> C6H12O6 + O2 Cycling carbon comes in four pathways 1) Photosynthesis: Plants use carbon dioxide and water to make sugar and oxygen CO2 + H2O -> C6H12O6 + O2 2) Cellular respiration: Animals and plants breakdown sugar to make carbon dioxide and water C6H12O6 + O2 -> CO2 + H2O Cycling carbon comes in four pathways 3) Decomposition: Bacteria and fungi break down organisms into organic matter Cycling carbon comes in four pathways 3) Decomposition: Bacteria and fungi break down organisms into organic matter 4) Food Web: Carbon moves between plants and animals during the food web interaction (Eg. Carbon from plants moves into deer) Carbon Exchange • Carbon Moves in and out of stores at certain rates: – The up arrow shows carbon leaving the store. – The down arrow shows carbon entering a store Carbon Stores • Long term storage of carbon. This carbon is not yet available to the biotic factors in the ecosystem.