Free Labor Ideology and the Politics of the Mexican War
advertisement

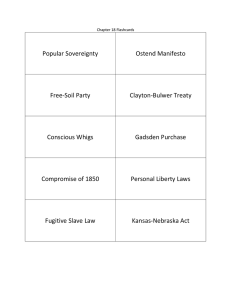
Free Labor Ideology and the Politics of the Mexican War The Long March to Civil War Begins Previous Conflict Over Territory: Missouri Compromise, 1821 The major issues of the Second Party System were … A. Economic (Bank War) B. Social (Temperance & Reform) C. Slavery (Abolitionism, Cycle of Distrust) Lessons Learned from Missouri Compromise Debates Keep slavery out of national politics (“Conspiracy of Silence”). Make sure that each region has enough land for future expansion. Needed both northern and southern support to win national elections. Defining Free Labor Ideology Definition: Set of ideals that celebrated the North’s economic progress and the ability of ordinary men to become financially independent. These ideals include the belief that slavery invariably degraded free labor. Glorification of Hard Work and Economic Progress Hard Work Always Led to Economic Mobility Both Manual and Mental Labor Good Failure = Laziness, Personal Failing Yet Free Labor Reflected Fears of Economic Change Growth of Cities with Large Working Class: Can These Workers Acquire Independence? Solution: WESTERN LAND Tied to Manifest Destiny Western Land Provided Opportunity for All “The public lands [in the West] are the safety valve of our industrial and social engine.” Horace Greeley, Editor, New York Times Free Labor’s Economic Critique of Slavery Slavery degraded free labor and bred laziness. South lacked economic vitality. “Slave Power Conspiracy” Recipe for Political Disaster: South Wanted West as Well Southerners needed fresh land for cotton. Southerners worried about declining political and economic influence. Southern honor: insult to exclude slavery from western territories. James K. Polk and the Election of 1844 Slaveholder from Tennessee; Rabid Expansionist Elected in 1844 on Expansionist Agenda Polk Wanted to Annex Texas and Goad Mexico into War “Mexico Will Poison Us” Popular War, but Undercurrent of Opposition U. S. Acquired Huge Territory Northerners Feared Spread of Slavery Northerners Supported the Wilmot Proviso David Wilmot, PA Democrat: No Slavery in Newly Acquired Territory Huge Debate that Deadlocks Nation Nashville Convention of 1850 Compromise of 1850 and Mexican War Controversy California entered into the Union as a free state. Utah and New Mexico: Open to slavery via popular vote. Slave TRADE ended in Washington, D.C. Stronger Fugitive Slave Act New Fugitive Slave Act Created More Controversy New Law Established Federal Commissioners Northerners MUST Return Fugitive Slaves Northern Interpretation of Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 Single Biggest Event that Led to New Republican Party and War: The Kansas Nebraska Act of 1854 The Kansas-Nebraska Act Repealed the MO Compromise The Kansas-Neb Act Unleashes “One Helluva Storm” Mass public meetings led to the Republican party. Northern Whigs become Republicans. Southern Whigs join Democrats.