CHAPTER 14:
EARTH’S
HISTORY
Earth’s History
• Earth’s history is long and fascinating.
• There have been great biological and
geological changes
Fossil Records
• The fossil record provides
strong evidence of the
evolution of life
Triceratops
Nicholas Steno
• Earth’s history has been unveiled by scientists applying the tools of
critical thinking
• Nicholas Steno was a Danish theologian
• First to suggest that fossils had once been
living organisms
• Developed the Principles of Original Horizontality,
Superposition, and Lateral Continuity
James Hutton
• Scottish naturalist and physician
• Father of geologic time
• Proposed that geologic time was
indefinitely long
• Believed the Earth was self-renewing
(basis of rock cycle)
• Formulated the principle of
uniformitarianism
Charles Lyell
•
•
•
•
•
British lawyer
Father of Modern Geology
Wrote Principles of Geology
Popularized Principle of Uniformitarianism
Developed the Principles of Cross-cutting
Relationships and Inclusions
Charles Darwin
• English naturalist and geologist
• Studied Lyell’s Principles of Geology
• Wrote On the Origin of Species by Means
of Natural Selection
• Credited with the Theory of Evolution
Natural Selection
• All living things develop over time
from a very few simple forms
All individuals
survive equally
Conditions change
and only welladapted individuals
survive
New generation is
dominated by welladapted individuals
Can you think of a change in
conditions that might lead
to natural selection?
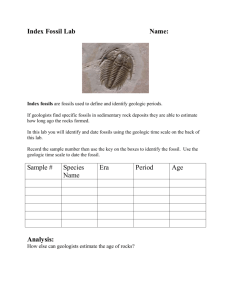
Fossils
• Fossils are the
remains of
animals and
plants, or traces
of their
presence, that
have been
preserved in the
crust.
• Fossils preserve
a record of past
life.
How Are Fossils Made?
• Fossilization is the process that turns
a once-living thing into a fossil.
• The Fossil record is biased. Rapid
burial is required. In most cases just
shell, teeth, and bones are
preserved.
• Preservation is typically by:
replacement or formation of a mold
or cast.
Brachiopod shells
Rare, soft part
preservation
(dinosaur skin)
Are these molds or casts or both? Is
there evidence of replacement here?
There are several lines of evidence for
evolution
• Phylogeny
Phylogeny is the history of organismal lineages as they change through time.
What are some of the changes evident in the phylogeny of the horse?
Homologous Structures
Vestigial Structures
How does the
existence of vestigial
structures support
the concept of
evolution?
Embryology
• Even distantly related organisms have
similar embryonic forms that can be
traced back to their evolutionary
history
Molecular biology also provides evidence of
evolution
• Changes within separate populations of the same species result in new
species through natural selection.
• Genetic Mutation
– (random changes to RNA or DNA)
• Genetic Variation
– (differences in inherited traits)
Molecular biology documents the relationship of
living organisms to their ancestors
Parasitic microbes, viruses, bacteria ... all
evolve!
Extinctions
• Mass extinctions are dramatic events in the otherwise slow process of evolution
Which of the Phanerozoic extinctions had the greatest impact on marine
organisms? Which one lead to the extinction of the terrestrial dinosaurs?
Extinction
• During a mass extinction large numbers of species die out within a relatively
short period of time.
There are various hypotheses for each mass
extinction ...
Geologic Time Scale
• The Geologic Time Scale is the
“calendar” of events in Earth’s history
Geologic Column
Drag and Drop
Animation
Hadean Eon
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Heating of the interior
Magma “ocean”
“Iron Catastrophe”
Eventual cooling
Earliest crust and oceans
Ended ~ 3.8 bya
Began ~ 4.6 bya
Extraterrestrial barrage
Atmosphere rich in methane, ammonia and carbon dioxide
Why was the Earth so much hotter
during the Hadean than it is now?
The Archean and Proterozoic Eons lasted
from 3.8 million to 542 million years ago
Archean and Proterozoic cratons (i.e., continent crustal blocks)
Archean Eon
• Atmosphere noxious to modern organisms (methane, ammonia, carbon
dioxide, and water vapor)
• More extraterrestrial bombardment
• More volcanic outgassing
• Continental Cratons form
• Abundant life first appears (stromatolites)
• Photosynthesis initiated
The atmosphere of the Archean
would have been noxious to us.
What component of our
atmosphere would have been
noxious to the Archeans?
Ancient and modern stromatolites
Proterozoic Eon
•
•
•
•
Continents develop, clustered together (Rodinia) in the southern hemisphere
Mountain building
Atmosphere becomes gradually more oxygenated
Diversification of soft-bodied organisms
Phanerozoic Eon
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
~ 542 mya to present
Includes the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras
Major mountain-building events
Pangaea continues break up into modern continents
Complex life evolves with much diversification
Geographic separation isolates some populations
Punctuated by mass extinctions
Tiktaalik roseae - a
critical transitional
organism from
Canada’s Arctic
In the Paleozoic Era complex life evolved
and the continents reorganized
The Cambrian Explosion
• Organisms that evolved during the Cambrian Explosion, developed some of
the basic inherited traits that are still present today, and others that vanished
forever.
Steven Earle
Steven Earle
Steven Earle
Steven Earle
What is so important about the
fossils of the Burgess Shale in
the Canadian Rockies?
In the Mesozoic Era biological diversity increased
and continents reorganized yet again
Mesozoic diversity
Steven Earle
Plesiosaur
Allosaurus claw
Dicot leaf
The Tethys Sea
• Continents separated and moved towards their present configuration. The
Tethys Sea (the ancestor to the Pacific Ocean) wrapped the globe along the
equator.
Tethys Sea
Mammals and birds diversified and primates
arose during the Cenozoic Era
a
b
c
d
(a) Sahelanthropus tchadensis (b) Australopithecus afarensis
(c) Homo erectus (d) Homo sapiens sapiens
Earth in the Quaternary Period
Why was sea level relatively low during much of the Quaternary?
COPYRIGHT
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons Canada, Ltd. All
rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work
beyond that permitted by Access Copyright (The Canadian
Copyright Licensing Agency) is unlawful. Requests for
further information should be addressed to the
Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons Canada, Ltd.
The purchaser may make back-up copies for his or her
own use only and not for distribution or resale. The
author and the publisher assume no responsibility for
errors, omissions, or damages caused by the use of these
programs or from the use of the information contained
herein.