Executive Branch Vocabulary

Executive Branch
Responsible for executing or carrying out the law
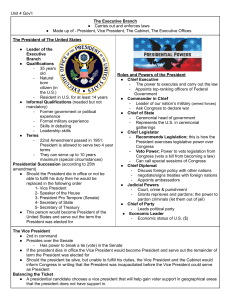
Qualifications to be President:
Natural Born citizen
At least 35 years old
Must have lived in the
U.S. for at least 14 years
4 years a term – no more than 2 terms
7 Roles of President
(many defined by the Constitution):
1. Chief Executive:
•Makes sure laws are carried out
•Creates policies
•Hires and fires executive officials
•Appoints federal judges
•Makes executive orders
Executive Order: a rule or order has the status of a law (does not violate the
Constitution or laws passed by
Congress)
2. Commander in Chief:
• Head of military forces
• Framers wanted to maintain civilian authority over the military
• Cannot declare war (only Congress can, but presidents have sent troops into other countries)
3. Head of State:
•Living symbol of the U.S.
•Ceremonial Duties (welcoming foreign leaders, etc.)
4. Chief Diplomat
Director of Foreign Policy
• Foreign policy: the set of plans for guiding relationships with other countries.
• Can make treaties with other nations
(Senate must approve) and executive agreements/goals for trade (non-
Senate approval)
Can appoint ambassadors (official representatives to foreign governments)
Ambassador: a diplomat of the highest rank acting as a representative from one's country to another
5. Head of Political Party
•Uses influence to back party candidates and raise money for campaigns
•Uses power to support and influence party goals
6. Economic Guardian
• Prepares a federal budget (plan for how to raise and spend money to carry out the President’s programs)
• Appoints the head of the Federal
Reserve, which controls the amount of money circulating in the U.S.
7. Legislative Leader
• State of the Union Address- gives ideas of foreign and domestic policies should be.
• Domestic policy: a set of plans for dealing with national problems
• Has the power to sign acts of
Congress into law or veto any law.
• Veto: refuse to sign a bill passed by
Congress, preventing it from becoming law
• Congress can override the veto with
2/3 majority vote.
Presidential Pardon: a release from legal punishment
Impeachment: the presentation of formal charges against a public official by the House, trial to be before the Senate
The Man Who Saved the Presidency page 84.
President's Daily Brief (PDB): is a top-secret document produced each morning for the President with new international intelligence warranting attention.
The President can’t do all of this alone!!!
Bureaucracy: an organization of government departments, agencies, and offices.
Remember the President is only the head of the executive branch!
The Organization of the
Executive Branch
15 Departments: each one focuses on specific activity, such as
• Education
• Defense
• Energy
President appoints a secretary (head of department) that makes up the
Presidential Cabinet.
Cabinet: helps the president make decisions about how laws should be carried out.
(refer to icivics worksheet for specifics)
Carrying Out Laws???
Enforce the law when some isn’t following it
Create regulations (rules) about how a law should be carried out. Have power similar to laws.