Hybridization Inbreeding Advantage Disadvantage
advertisement

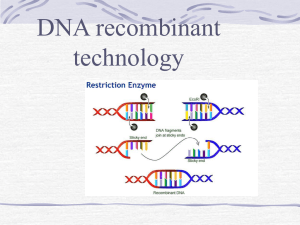
Name: Pd: _ Biology 15.1/15.2 Review 1. If a farmer is using selective breeding with his plants and animals, what is he doing? 2. The two types of selective breeding are hybridization and inbreeding. A. Describe each and B. include an example of each (made up or real) Example you cannot use: Hybridization: rabbit + antelope = jackalope 3. Fill in the table below Hybridization Inbreeding Advantage Disadvantage Hybrids are often steril. 4. There are two main ways to increase variation. A. In bacteria, for example, scientists can introduce . B. For plants, scientists can make them , which means 5. For each process, put the steps on the right in the correct order on the left. Copying DNA PCR 1. A. Use PCR to copy 1. A. Add DNA polymerase 2. B. Extract DNA 2. B. Separate DNA strands 3. C. Use restriction enzymes 3. C. Use copies to make more copies 6. What do restriction enzymes do? Name: Pd: _ 7. We use recombinant DNA to transform bacteria to produce human proteins. What is recombinant DNA? 8. What are plasmids, and where are they found? 9. Sometimes when making bacteria with recombinant DNA, they get mixed in with regular bacteria. What can I use a genetic marker for? 10. What is a transgenic organism? Give an example (made up or real). Example you cannot use: Dog + chameleon gene for color change = dog that can change color. 11. A. Define clone: B. Does that mean the clone will be exactly like the first in every way? C. Cloning requires a procedure called nuclear transplantation. Arrange the steps in order below. 1. A. Egg (without nucleus) is fused with donor cell (with nucleus) 2. B. Egg with donor nucleus is placed in foster mother 3. C. Nucleus of egg is removed.