5.1.3 Pollution from Fossil Fuels
advertisement

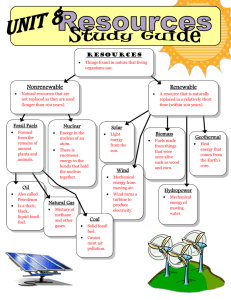
5.1.3 POLLUTION FROM FOSSIL FUELS The Era of Fossil Fuels • Fossil fuels: petroleum, natural gas and coal (organic) • Currently 90% of current US energy from from fossil fuels • Expected oil production peak: 2020-2030 • Consumption currently increasing • Projected world oil production will be exhausted by 2100 • Produces significant and diverse pollution problems o Greenhouse gasses o Gaseous Sulfur and nitrogen oxides o Land-based disturbances What Is Crude Oil? Crude Oil is a liquid mixture of thousands of organic chemicals found underground. It is the result of organic matter decaying over thousands of years; hence the name fossil fuel Crude oil is found all over the world and varies tremendously in its density, sulfur, and metals content Very Simplified Petroleum and Petrochemical Flowchart THE REFINERY Natural Gas RX Propane & Butane RX Naphtha (C5 - C10) Ethylene RX Gas Stove Polyethylene (Glad Bags) Polymers (7 UP Bottles) RX RX Gasoline Organic Chemicals (Aspirin, Hair Spray) More Polymers (Football Helmet, Astro Turf, Nylon) Jet Fuel Gas Oils (C10+) Separations and Purifications Crude Separations Oil Conversions Kerosene & Oil Well Diesel Fuels Home Heating Oil, Lubricating Oil, Wax Coke (Carbon Material Similar to Coal) Asphalt Purifications remove sulfur and heavy metals RX = Chemical Reactions Fuel (Barbeque Grills) Roads Fuel Steel Making Graphite Fibers (Tennis Racquets) Pot Holes Proven world oil reserves in 1998. © 2003 John Wiley and Sons Publishers Coal World’s most abundant fossil fuel, but dirtiest! Coal provides 25% of world’s commercial energy; 22% of US energy Dangerous to mine, harms land, water and air – causes smog, acid rain and global warming. Burning coal releases thousands of time more radioactive particles per unit of energy than a nuclear power plant! Fig 17.9 World coal reserves in 1999. © 2003 John Wiley and Sons Publishers Pollution Health Impacts More than 131 million Americans live in areas where smog pollution makes their air unsafe to breathe, and every year over 45,000 lives are cut short by air pollution. The National Academy of Sciences estimates that every year 60,000 children may be born at a significantly increased risk of neurological defects primarily due to mothers eating mercury-contaminated fish. Pollution Oil Spills 31,000 galloons of spilled into waterways every day Between 1973 and 1993 there were 200,000 oil spills in U.S. waters, spilling more than 230 million gallons of oil. Pollution Land Destruction Mountaintop removal in West Virginia Tens of thousands of coalbed methane wells in the Powder River Basin in Wyoming Pollution Global Warming With only 4 percent of the world's population, we produce 25 percent of the carbon dioxide pollution Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change projects that the Earth's average surface temperature will increase between 2.5 and 10.4°F (1.4 to 5.8°C) between 1990 and 2100 if no major efforts are undertaken to reduce the emissions of greenhouse gases (the "business-as-usual" scenario). Total energy consumption for the United States, 19501999. © 2003 John Wiley and Sons Publishers “This [U.S. oil] is an industry that probably has larger tax incentives relative to its size than any other industry in the country.” Statement of Hon. Donald C. Lubick, former Assistant Secretary for Tax Policy, U.S. Department of Treasury Taxes for 1 gal of gasoline in U.S. dollars equivalent for selected countries, 1995. © 2003 John Wiley and Sons Publishers Current Energy Tax Breaks Fiscal Years 2003-2007 1% 1% 2% 2% 12% 6% 76% Nuclear Tax Exempt Energy Bonds Oil and Gas Coal Energy Conservation Geothermal and Solar Wind and Biomass Historical Research and Development Dollars Department of Energy Research and Development (Fiscal Year 1948-1998) Energy Efficiency Renewables 7% 11% $12 Billion $8 Billion $66 Billion $26 Billion Nuclear Energy 59% Fossil Fuel 23% Nuclear Energy Fossil Fuel Energy Efficiency Renewables