Chemistry ch 14 Liquids and Solids
advertisement

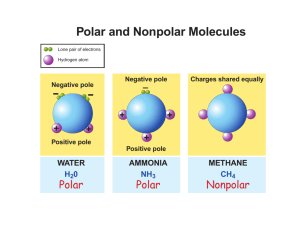
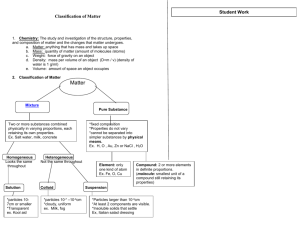
Liquids Definite volume Fluidity – able to flow Relative high density Relative incompressibility Dissolving ability Ability to diffuse Tendency to evaporate and boil Tendency to solidify Solids 2 types of solids Crystalline solid (crystal) Arranged in an orderly, repeating pattern Amorphous solid (without form) Arranged randomly – no pattern Properties of solids Definite shape Definite volume Nonfluidity Definite melting point High density Incompressibility Crystalline solids The total 3-dimensional array of points that describe the arrangement of particles in a crystal is called a crystal lattice. 1 repeating piece is a unit cell Phase Diagram (Freezing Points) Pressure (atm) Liquid 1 (Boiling Points) Solid . Gas (Triple Point) 0 100 Temperature (oC) Mixtures 3 Types of mixtures 1. Solution Soluble – will dissolve Forms a homogeneous mixture Very small particles 2 Parts of a solution Solute – stuff that dissolves Solvent – stuff that the solute dissolves in Types of solutions Solute Solvent Example Gas Gas Air Gas Liquid Soda Water Gas Solid - Liquid Gas Humidity Liquid Liquid Juice in water Liquid Solid - Solid Gas Sulfur in air Solid Liquid Kool Aid Solid Solid Alloy (Brass) 2. Suspensions Heterogeneous mixture that settles Large particles Muddy water, italian salad dressing (anything that must be shaken) 3. Colloids Intermediate sized particles Particles disperse 2 parts of a colloid Tyndall Effect Seeing a beam of light (separates colloid from solution) Examples of Colloids Colloid Phase Gel solid dispersed in liquid Liquid emulsion liquid dispersed in liquid Foam gas dispersed in liquid Smoke solid dispersed in gas Fog liquid dispersed in gas Smog solid & liquid dispersed in gas 3 types of mixtures Solutions Colloids Homogeneous Homogeneous Intermediate Very small sized particles Does not Does not separate separate Tyndall effect No light scattering Suspensions Heterogeneous Large particles Separates No Tyndall effect The solution process Increasing the Rate of dissolving 1. Increase the surface area of solute 2. Agitating the solution 3. Heating the solvent Types of solutions Electrolyte A solution that has ions in it and can conduct electricity Saturated solution Contains the maximum amount of solute Unsaturated solution Contains less than the maximum amount of solute Supersaturated solution Contains more than the maximum amount of solute (Rock candy, crystals) Factors affecting solubility 1. Types of solvents and solutes Like dissolves like Refers to polarity Water is a polar molecule Oil is a nonpolar molecule If they are the same polarity, the compounds are miscible (mixable) - salt in water, vinegar in water If they are not soluble, they are immiscible (not mixable) - oil in water, salt in oil 2. Pressure Under pressure a gas will enter and dissolve in a liquid fizz in a bottle of pop If pressure is released, the liquid can’t hold as much gas 3. Effervescence Temperature Warmer liquids hold less gas Burp more from warm pop