Chapter 4 - Fort Bend ISD
advertisement

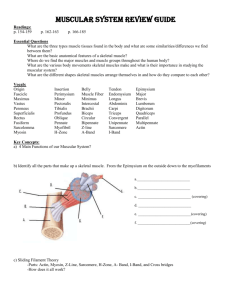
Fall Semester Exam Review Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Skinner Multiple Choice Chapter 1 1. a. b. c. d. e. Which of the following organs would be found in your thoracic cavity? Stomach Heart Urinary bladder Brain None of the above 2. a. b. c. d. e. When we refer to the ventral surface of the human body, we are talking about the ____________ surface? Superior Inferior Anterior Posterior None of the above 3. a. b. c. d. e. Which of the following organs is found in the abdominal cavity? stomach heart urinary bladder brain none of the above 4. a. b. c. d. e. From largest to smallest, the levels of organization of the body are: organism, system, organ, tissue, cell, organelle, molecule molecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, system, organism organism, system, organ, cell, tissue, molecule, organelle chemical, system, organ, tissue, cell, organelle, molecule none of the above 5. a. Physiology: is concerned with organisms and does not deal with different levels of organization such as cell and systems is the science that examines the function of living organisms and their parts recognizes the unchanging nature of things investigates the body’s structure none of the above b. c. d. e. 6. a. b. c. d. e. Which of the following describes anatomy? studying the unusual manner in which an organism responds to painful stimuli examining the physiology of life using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate and blood pressure investigating human structure via dissections and other methods none of the above 7. a. b. c. d. e. Which of the following describes anatomy? studying the unusual manner in which an organism responds to painful stimuli examining the physiology of life using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate and blood pressure investigating human structure via dissections and other methods none of the above 8. a. b. c. d. e. The smallest living units of structure and function in the body are: organelles atoms molecules cells none of the above 9. a. b. c. d. e. What is the study of life? Anatomy Physiology Biology Chemistry None of the above 10. a. b. c. d. e. Homeostasis can best be described as: adaptation to external environment changes in body temperature a constant state maintained by living and nonliving organisms a state of relative constancy sum total of the chemical processes occurring in the body Chapter 2-3 1. A. B. C. D. E. DNA is a major constituent of which cell organelle? lysosome ribosome chromosome nucleus none of the above 2. A. B. C. D. E. Which tissue lines body cavities and protects body surfaces? muscle connective epithelial nervous A and B 3. A. B. C. D. E. What makes up the matrix of blood? membrane plasma platelets red blood cells C and D 4. A. B. C. D. E. In the skin, the dermis: and epidermis are both connective tissue is connective tissue and the epidermis is epithelial tissue and epidermis are both epithelial tissue is epithelial tissue and the epidermis is connective tissue A and C 5. A. B. C. D. E. The layer beneath the dermis is called the: reticular layer hypodermis subcutaneous layer A and B B and C 6. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following is true of stratified, cuboidal epithelium? it is one layer thick it is multiple layers thick it has squamous cells on its superficial surface none are true A and C 7. A. B. C. D. E. Cartilage is a form of: epithelial tissue connective tissue muscle tissue osseous tissue nervous tissue 8. A. B. C. D. E. Blood is a member of which basic tissue type? epithelial connective muscle nervous none of the above 9. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following would be found in the epidermis? stratified columnar epithelium stratified cuboidal epithelium stratified squamous epithelium simple squamous epithelium none of the above 10. A. B. C. D. E. The type of tissue that contains cells called neurons is: muscle epithelial connective nervous none of the above 11. A. B. C. D. E. Connective tissue membranes differ from cutaneous and serous membranes in that they: are not thin sheets of tissue do not contain epithelial components do not secrete fluids all of the above none of the above 12. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following is not true of simple squamous epithelium? it is one layer thick it prevents the diffusion of material from one part of the body to another it is composed of flat, scale-like cells all are true none are true 13. A. B. C. D. E. The serous membrane lining the abdominal cavity would be called the: visceral pleura visceral peritoneum parietal pleura parietal peritoneum none of the above 14. A. B. C. D. E. The skin is made up of which two layers: epidermis and hypodermis dermis and epidermis hypodermis and dermis dermis and subcutaneous fascia both C and D 15. A. B. C. D. E. A tough protein that adds structural strength to hair, skin, and nails is: melanin collagen keratin elastin none of the above 16. A. B. C. D. E. What is the main form of sugar that circulates in the blood? sucrose fructose glycogen starch none of the above 17. A. B. C. D. E. Organic compounds contain both __________ and _____________. hydrogen and oxygen oxygen and carbon nitrogen and carbon nitrogen and oxygen hydrogen and carbon 18. A. B. C. D. E. Human somatic cells contain ______ chromosomes. 8 23 46 92 none of the above 19. A. B. C. D. E. Peptide bonds join together molecules of: glycerol glucose amino acids water monosaccharides 20. A. B. C. D. E. All of the following substances are organic except: lipids water carbohydrates proteins none are organic 21. A. B. C. D. E. Mucous membranes line which of the following hollow organ tracts? digestive tract urinary tract respiratory tract all of the above none of the above 22. A. B. C. D. E. Amino acids are the monomers for: carbohydrates proteins nucleic Acids lipids none of the above 23. A. B. C. D. E. An exocrine gland: secretes its product into the interstitial space lines body cavities secretes its product to the outside world covers body surfaces none of the above 24. A. B. C. D. E. The basic unit of structure and function in the human body is a(n): atom cell gene DNA molecule none of the above 25. A. B. C. D. E. The major energy production site of the cell is the: Golgi apparatus mitochondrion endoplasmic reticulum ribosome none of the above Chapter 4 1. A. B. C. D. E. Which is not a part of the appendicular skeleton? navicular trapezoid ethmoid tibia calcaneus 2. A. B. C. D. E. The appendicular skeleton consists of: 102 bones 118 bones 124 bones 137 bones none of the above 3. A. B. C. D. E. Which bone is a part of the appendicular skeleton? sternum vertebra parietal mandible none of the above 4. A. B. C. D. E. The layman’s name for the tibia is the: collar bone kneecap shinbone elbow breast bone 5. A. B. C. D. E. The ulna articulates proximally with the: carpal bones humerus scapula clavicle none of the above 6. A. B. C. D. E. Metatarsal bones form the framework of the: wrist hand ankle foot none of the above 7. A. B. C. D. E. The pisiform bone can be found in the: wrist ankle neck skull foot 8. A. B. C. D. E. The anterior of the pelvic girdle is formed by the: sacrum ilium ischium pubis coccyx 9. A. B. C. D. E. The longest and heaviest bone in the body is the: tibia fibula coxal femur humerus 10. A. B. C. D. E. A person with a fractured olecranon process would expect discomfort in the: elbow knee head ankle shoulder 11. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following is not a tarsal bone? cuneiform navicular scaphoid talus calcaneus 12. A. B. C. D. E. Going from distal to proximal, the bones of the upper extremity would be: metacarpals, carpals, ulna, and humerus carpals, metacarpals, ulna, and humerus humerus, radius, metacarpals, and carpals humerus, radius, carpals, and metacarpals radius, ulna, humerus, metacarpals 13. A. B. C. D. E. Going from proximal to distal, the bones of the lower extremity would be: femur, tibia, carpals, and metacarpals metatarsals, tarsals, tibia, and femur femur, tibia, tarsals, and metatarsals metacarpals, carpals, tibia, and femur none are correct 14. A. B. C. D. E. Which is not a part of the axial skeleton? talus clavicle scapula cuboid none are part of the axial skeleton 15. A. B. C. D. E. The axial skeleton consists of: 46 bones 64 bones 80 bones 88 bones 92 bones 16. A. B. C. D. E. Which bone is a part of the axial skeleton? xiphoid process clavicle radius coxal bones scapula 17. A. B. C. D. E. The thoracic cage includes all of the following bones except: the scapula 12 pairs of ribs the vertebral column the sternum all are part of the thoracic cage 18. A. B. C. D. E. The trochlea and capitulum can be described as: markings on the scapula parts of the proximal end of the ulna distal portions of the humerus metacarpal bones parts of the distal portion of the femur 19. A. B. C. D. E. Going from superior to inferior, the sequence of the vertebral column is: sacral, coccyx, thoracic, lumbar, and cervical coccyx, sacral, lumbar, thoracic, and cervical cervical, lumbar, thoracic, sacral, and coccyx cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccyx both B and D 20. A. B. C. D. E. Which suture is between the occipital and parietal bones? squamous lambdoidal sagittal coronal parietal 21. A. B. C. D. E. The upper part of the sternum is called the: costal cartilage xiphoid process body manubrium acromioclavicular joint 22. A. B. C. D. E. The skeletal framework of the neck consists of: lumbar vertebrae thoracic vertebrae sacral vertebrae cervical vertebrae none of the above 23. A. B. C. D. E. The number of thoracic vertebrae is: 5 7 8 10 12 24. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following bones is not a part of the face? trapezium zygomatic lacrimal maxilla both A and C 25. A. B. C. D. E. The occipital bone forms which number of joints with other bones? 1 2 3 4 none are correct Chapter 5 1. A. B. C. D. E. Muscles may be named according to: function direction of fibers location all of the above none of the above 2. A. B. C. D. E. A muscle that assists with mastication is the: orbicularis oris nasalis platysma masseter none of the above 3. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following muscles does not move the upper arm? pectoralis major latissimus dorsi deltoid biceps brachii none of the above 4. A. B. C. D. E. The muscle that adducts and flexes the upper arm is the: triceps brachii biceps brachii trapezius pectoralis major none of the above 5. A. B. C. D. E. The muscle that flexes the head is the: biceps brachii latissimus dorsi trapezius sternocleidomastoid none of the above 6. A. B. C. D. E. The posterior arm muscle that extends the forearm is the: biceps brachii triceps brachii deltoid brachialis none of the above 7. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following is not a muscle of the quadriceps? rectus femoris biceps femoris vastus medialis vastus intermedius none of the above 8. A. B. C. D. E. When an athlete injures a muscle of the hamstring group, the injury is on the: upper arm posterior lower leg posterior thigh anterior thigh none of the above 9. A muscle is attached to the femur and the tibia. When the muscle contracts, the knee bends. That would mean that the: tibia attachment is the origin femur attachment is the insertion tibia attachment is the insertion A and B none are correct A. B. C. D. E. 10. A. B. C. D. E. A long straplike muscle that crosses the anterior thigh diagonally and assists with flexion, abduction, and lateral rotation of the thigh is the: rectus femoris vastus lateralis vastus intermedius vastus medialis none of the above 11. A. B. C. D. E. The connective tissue sheath that envelops a fascicle is the: epimysium endomysium periosteum perimysium none of the above 12. A. B. C. D. E. The covering of individual muscle fibers is the: epimysium endomysium periosteum perimysium none of the above 13. A. B. C. D. E. A muscle of the posterior lower limb whose function is flexion of the lower leg is the: biceps femoris rectus femoris gastrocnemius tibialis anterior none of the above 14. A. B. C. D. E. The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber is called the: sarcomere sarcoplasm sarcolemma endomysium none of the above 15. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following is also known as striated muscle? smooth muscle skeletal muscle involuntary muscle visceral muscle none of the above 16. A. B. C. D. E. The ability of muscle cells to respond to nerve stimulus is called: irritability contractility extensibility elasticity none of the above 17. A. B. C. D. E. A motor unit is most correctly described as a: sarcomere(s) and a motor neuron myofibril(s) and a motor neuron muscle fiber(s) and a motor neuron filaments(s) and a motor neuron none of the above 18. A. B. C. D. E. A contraction in which the tension within the muscle remains the same but the muscle shortens is called a(n): eccentric contraction concentric contraction isometric contraction both B and C none of the above 19. A. B. C. D. E. A muscle of the lower limb whose function is to extend the femur is the: rectus femoris gastrocnemius gluteus maximus biceps femoris none of the above 20. A. B. C. D. E. Which type of skeletal muscle fibers have the fastest rate of contraction? Type Ia Type Ib Type IIa Type IIb Type III 21. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following types of muscle tissue contains cells that have a multiple nuclei? cardiac smooth skeletal A and B none of the above 22. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following is not a characteristic of smooth muscle: they are voluntarily controlled they are not controlled voluntarily they have cells with only one nucleus they are not striated all are true of smooth muscle 23. A. B. C. D. E. Cardiac muscle is muscle tissue that is located: in the stomach in the lungs in the intestines in the heart none of the above 24. A. B. C. D. E. An muscle of the posterior upper arm whose function is to extend the forearm is the: biceps brachii brachialis brachioradialis triceps brachii none of the above 25. A. B. C. D. E. Visceral muscle is another name for: skeletal muscle smooth muscle cardiac muscle both B and C none of the above 26. A. B. C. D. E. A muscle whose function is raising the eyebrows is the: orbicularis oris orbicularis oculi frontalis masseter none of the above 27. A. B. C. D. E. What is the connective tissue that wraps the entire muscle: endomysium perimysium epimysium periosteum none of the above 28. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following list of muscles make up the quadriceps muscle group? rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, sartorius rectus femoris, vastus intermedius, vastus lateralis, biceps femoris biceps femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius biceps femoris, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, sartorius none are correct 29. A. B. C. D. E. The triceps brachii acts as the __________ during flexion of the forearm. agonist antagonist insertion both of the above none of the above 30. A. B. C. D. E. A hamstring injury might affect which of the following muscles: rectus femoris sartorius vastus medialis gastrocnemius none of the above 32. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following muscles make up the hamstring muscle group? semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius biceps femoris, rectus femoris, semitendinosus semitendinosus, semimembranosus, sartorius none of the above 33. A. B. C. D. E. The muscle that causes plantar flexion of the foot is the: hamstrings quadriceps gastrocnemius tibialis anterior none of the above Matching Chapter 1 Directional Terms a. b. c. d. e. Superior Anterior Medial Proximal Superficial a. b. c. d. e. Distal Lateral Posterior Inferior Deep 1. The ankle is _____ to the knee. 2. The ear is on the _____ aspect of the head. 3. The vertebrae are located on the _____ aspect of the body. 4. The wrist is _____ to the elbow (further from attachment point). 5. The knee is _____ compared to the ankle. Body Systems a. b. c. d. e. a. b. c. d. e. a. muscular reproductive skeletal endocrine nervous respiratory cardiovascular digestive integumentary urinary immune 6. Stomach 7. Spinal cord 8. Lungs 9. Heart 10. Bones Body Planes a. b. c. Sagittal Frontal Transverse 11. If you were to cut a human skull in half leaving a right side and a left side of equal size, on what plane was the section made? 12. If you were to saw a human skull into anterior and posterior portions, what type of section was made? 13. What type of section would cut the human skull into superior and inferior sections? 14. If I cut myself in half at the waist, on what plane would the cut be made? Chapter 4 Matching Match the bone markings with the bones on which they can be found. A. B. C. D. E. A. B. C. D. E. femur fibula humerus coxal radius ribs scapula sternum tibia ulna 1. _____ olecranon process 2. _____ lateral malleolus 3. _____ medial malleolus 4. _____ obturator foramen 5. _____ acromion process Chapter 5 Match the following muscles with their location. A. B. C. D. E. A. B. C. D. E. neck back chest abdominal wall shoulder upper arm forearm buttocks thigh lower leg 1. _____ gluteus maximus 2. _____ biceps brachii 3. _____ trapezius 4. _____ pectoralis major 5. _____ semitendinosus 6. _____ external oblique 7. _____ deltoid The following features are used in the naming of muscles. Match the feature with the muscles or terms listed. A. B. C. D. location function direction of fibers number of heads or divisions 8. _____ triceps 9. _____ adductors 10. _____ brachialis 11. _____ quadriceps 12. _____ gluteus Match the following muscles with their action. A. B. C. D. abduction adduction flexion extension 13. _____ biceps brachii 14. _____ gluteus maximus 15. _____ sternocleidomastoids 16. _____ triceps brachii 17. _____ rectus femoris